What Is CMMC 2.0? A Guide to CMMC Compliance Requirements for Defense Contractors

If your company is a prime or subprime contractor for the Department of Defense (DoD), you should be familiar with CMMC. That’s because CMMC requirements are now included in all new DoD solicitations and contracts because of the 48 CFR rule.
What does that mean for your business, and how should you prepare? In this post, we cover everything you need to know about CMMC.
What is CMMC 2.0?
The first question many people have is, “What does CMMC stand for?” CMMC stands for Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification. CMMC is designed to ensure that cybersecurity controls and processes adequately protect Federal Contract Information (FCI) and Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) that resides on Defense Industrial Base (DIB) systems and networks.
CMMC 1.0 was finalized in 2020. CMMC 2.0 — published in October 2024 — is an updated framework with three control levels, as opposed to the five maturity levels in CMMC 1.0.
What is a C3PAO?
A C3PAO is a CMMC Third Party Assessment Organization, The Cyber AB authorizes a C3PAO to contract and manage CMMC assessments and only authorized C3PAOs can conduct CMMC assessments.
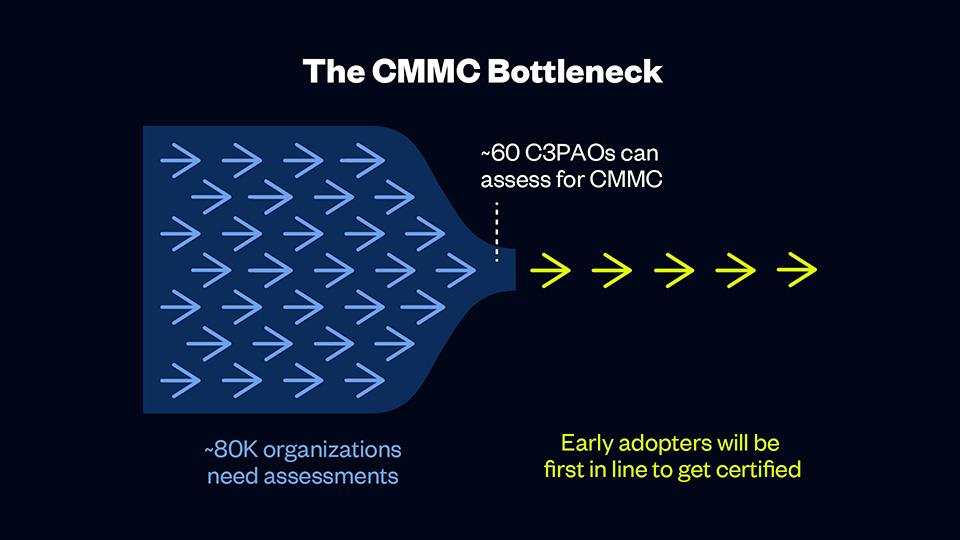
Currently, fewer than 85 C3PAOs can assess for CMMC, and more than 80,000 organizations need assessments. That means early adopters will have their pick of C3PAOs and will be first in line to receive certification, and organizations who are slow to act may face long waitlists or delays.
A C3PAO is an essential partner in your CMMC journey. C3PAOs follow the CMMC assessment process and conduct thorough assessments of DoD contractors. Although the Cyber AB authorizes all C3PAOs, each organization has different strengths and weaknesses, so you must choose an organization that meets your needs. Get a checklist of questions to ask a C3PAO in our CMMC Buyer’s Guide to ensure you’re choosing the right partner for your CMMC journey.
CMMC 2.0 requirements
With the CMMC 2.0 program, the DoD introduced several changes compared to the original version of the program. Most obviously, the model has been streamlined from five to three compliance levels that each correspond with existing, widely accepted cybersecurity standards. And while many organizations will require third-party assessment, many will be able to demonstrate compliance through self-assessment, reducing costs for these organizations. Additionally, the DoD will allow companies to receive contract awards with the creation of a Plan of Action & Milestones (POA&M) that describes how and when CMMC controls will be met.
The CMMC 2.0 model
The CMMC 2.0 framework organizes multiple cybersecurity standards and best practices into a set of practices and processes across three increasingly stringent levels. These practices and processes must be applied across 14 domains (i.e., control families):
- Access Control (AC)
- Awareness & Training (AT)
- Audit & Accountability (AU)
- Configuration Management (CM)
- Identification & Authentication (IA)
- Incident Response (IR)
- Maintenance (MA)
- Media Protection (MP)
- Personnel Security (PS)
- Physical Protection (PE)
- Risk Assessment (RA)
- Security Assessment (CA)
- System and Communications Protection (SC)
- System and Information Integrity (SI)
What are the levels of CMMC 2.0?
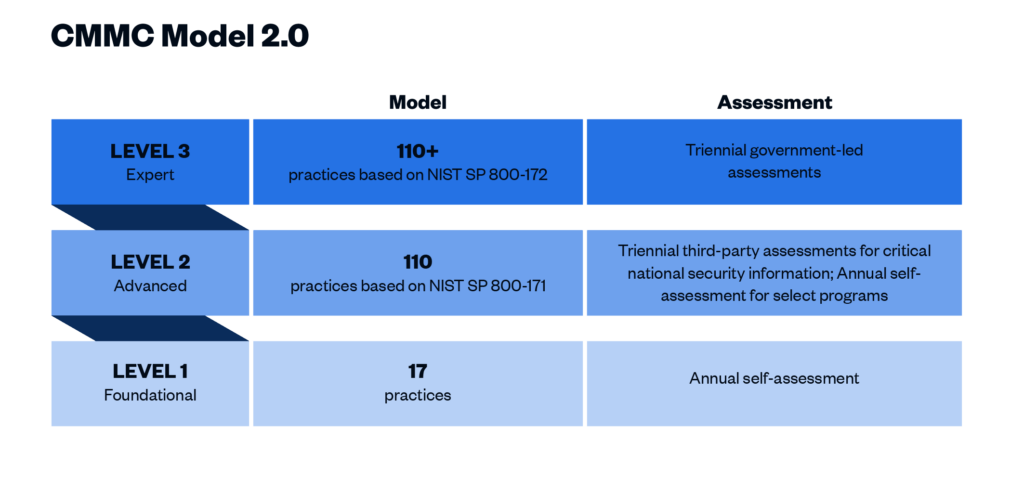
CMMC 2.0 Level 1 (“Foundational”) requirements
This level includes basic cybersecurity appropriate for small companies using a subset of universally accepted common practices that organizations must perform. Level 1 contractors are those that handle Federal Contract Information (FCI) but not CUI. One of the more significant changes from CMMC 1.0 to 2.0 is that Level 1 is now a self-assessment only, placing this responsibility on the organization itself. Level 1 includes the same 15 controls outlined in Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) 52.204-21.
CMMC 2.0 Level 2 (“Advanced”) requirements
Level 2 contractors are those that handle CUI. Processes at this level are maintained and followed, and there is a comprehensive knowledge of cyber assets. The DoD has pared down the 130 practices in the original CMMC Level 3 baseline to the 110 practices outlined in the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication 800-171. “Critical” handlers of CUI will need a third-party assessment by a CMMC Third Party Assessment Organization (C3PAO) for CMMC certification every three years. Level 2 processes must be documented and managed to protect CUI.
Note: The DoD’s definition of “critical” CUI has not yet been provided. The final rule will outline what CUI qualifies as critical.
CMMC 2.0 Level 3 (“Expert”) requirements
Level 3 is for organizations with the highest-priority programs with CUI. The processes involved at this level include continuous improvement across the enterprise and defensive responses performed at machine speed. This level will replace what was formally known as CMMC Level 5. Level 3 will add additional requirements pulled from NIST 800-172 in addition to the Level 2 requirements. It is expected that organizations will be required to be assessed by the DoD directly every three years for Level 3 requirements.
CMMC 2.0 vs. NIST 800-171
CMMC 2.0 is influenced heavily by the requirements in NIST 800-171. CMMC 2.0 Level 2 essentially mirrors NIST 800-171. If your organization processes CUI and does business with the DoD, you are already required to implement NIST 800-171 under Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement (DFARS) Clause 252.204-7012.
Additionally, the DFARS Interim Rule went into effect in November 2020. The interim rule requires DoD contractors to self-assess their implementation of NIST 800-171 and report their score through the Supplier Performance Risk System (SPRS). Performing this self-assessment and remediating any identified gaps simulates what CMMC 2.0 certification will be like.
What is 48 CFR?
The CMMC 48 CFR is the final rule and that makes CMMC enforceable in DoD contracts. The rule was published in the Federal Register on September 10, 2025 with an effective date of November 10, 2025. This marks the official start of Phase 1 of the CMMC roll out, meaning readiness is no longer optional and all new DoD solicitations and contracts include some level of CMMC requirement.
Who must comply with CMMC?
CMMC 2.0 is now mandatory for all entities doing business with the DoD at any level who store, transmit, or process information that meets the standards for FCI or CUI. Prime contractors and their subcontractors are required to meet one of the three CMMC trust levels and demonstrate that cybersecurity has been sufficiently implemented through the completion of independent validation activities. Initial award or continuance of a DoD contract will be dependent upon CMMC compliance.
No contractor organizations will be permitted to receive or share DoD information related to programs and projects without having completed the CMMC process. At the time that a contractor’s contract is up for renewal, they must be CMMC compliant.
CMMC 2.0 timeline
The Office of the Undersecretary of Defense for Acquisition and Sustainment (OUSD (A&S)) started the CMMC process in March 2019. The predicted date for the CMMC 2.0 rulemaking process to be completed has shifted several times, but the timeline below provides a history of significant milestones in the project thus far.
- January 2020: Version 1.0 was finalized and a compliance checklist was released.
- June 2020: CMMC began appearing in requests for information (RFIs).
- September 2020: CMMC began appearing in requests for proposals (RFPs).
- November 2020: The DFARS interim rule became effective; the original five-year phase-in period began.
- March 2021: DoD initiated an internal review of CMMC 1.0.
- November 2021: CMMC 2.0 was announced.
- September 2022: Cyber AB, the CMMC accreditation body, established training and accreditation processes.
- December 2023: The CMMC program proposed rule was released.
- May 2024: DoD’s Regulatory Control Officer submitted a draft of the proposed DFARS rule to the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs (OIRA).
- June 2024: 32 CFR 170, the rule finalizing the CMMC program, was submitted to OIRA for review.
- August 2024: The proposed rule for 48 CFR, the rule implementing the enforcement of the CMMC program into contract requirements was released.
- October 2024: 32 CFR, the rule finalizing the CMMC 2.0 program, was published.
- September 2025: 48 CFR, the rule that makes CMMC enforceable in CMMC contracts, is published in the Federal Register.
- November 2025: 48 CFR goes into effect, meaning readiness is no longer optional and all new DoD solicitations and contracts include some level of CMMC requirement.
Has CMMC 2.0 been released?
The 32 CFR final rule was published in October 2024.
When will CMMC 2.0 certifications be available?
To obtain a CMMC Level 2 Certification, you will need to be assessed by a C3PAO. Assessments are now underway as 48 CFR has made readiness mandatory.
How much does CMMC certification cost?
CMMC assessment costs are very scope-dependent as different organizations will have different sensitive data flowing through different numbers of assets. The DoD has assumed for the phased rollout of CMMC that roughly 35% of DIB contractors will require a certification assessment for Level 2, with the number of entities increasing incrementally over seven years (see p. 89085-89086 of Federal Register Vol. 88, No. 246).
With that said, the potential loss in business is too large for most organizations to forego certification. As mentioned earlier in this article, CMMC compliance is now required for all DoD prime and subprime contractors. For contractors that fall in CMMC Levels 2 and 3 and handle critical CUI, third-party certification is mandatory to continue doing business with the DoD.
Next steps: How to prepare for CMMC 2.0 certification
- Determine your organization’s CMMC level. Level 1 is for contractors and subcontractors processing FCI. Level 2 is for organizations processing CUI. Only organizations working on the DoD’s most sensitive programs will be expected to achieve Level 3 certification.
- Review the assessment guide for your CMMC level. The CMMC Level 1 Self-Assessment Guide and Level 2 Assessment Guide explain how contractors will be evaluated when CMMC is launched and organizations are pursuing certification. Unfortunately, there is not yet an assessment guide for CMMC Level 3.
- Work with a tech-enabled organization to secure your data. Cybersecurity solutions like Summit7, RISCPoint, and PreVeil can help you secure your FCI and CUI to prepare for CMMC compliance.
- Select a C3PAO and complete a readiness assessment. With a limited number of C3PAOs, it is important to start validating your organization’s readiness as soon as possible, as you will need time to remediate any gaps found.
- Sign a contract for CMMC certification ASAP. Once CMMC 2.0 certification starts showing up in DoD contracts, organizations that didn’t plan ahead will be scrambling to find a C3PAO and get in line for assessment.
How to select a C3PAO
Choosing the right C3PAO is crucial for a smooth and successful certification process. These are the key factors to consider when making your selection:
- Expertise: Look for a C3PAO with experience in federal compliance frameworks like FedRAMP, NIST, and StateRAMP to ensure they can guide you effectively through the certification process. You should also consider how long the C3PAO has been in business, the experience of its employees, and its overall knowledge of cybersecurity compliance.
- Quality: High-quality C3PAOs go beyond just checking boxes. They bring extensive experience and a deep understanding of CMMC requirements, which helps identify and address potential compliance issues effectively. They also provide thorough assessments and detailed feedback, helping you improve your cybersecurity posture and maintain compliance.
- Efficiency: Look for a C3PAO that uses technology to streamline the certification process. This will accelerate the process and minimize disruptions. To further increase efficiency, consider a firm who can tackle additional frameworks such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, and more.
- Timing: With 48 CFR’s effective date of November 10, 2025, it’s crucial to prepare now. Since this is a new rule, most organizations will need about 6-12 months of preparation before the assessment begins. Make sure your C3PAO can accommodate your timeline and place you in the assessment queue quickly.
- Budget: As with most things, you get what you pay for. Beware of budget C3PAOs that are offering assessments for under-market value. Balance your budget with other important factors listed above like quality, efficiency, timing, and expertise.
Why sign a CMMC certification contract now?
By getting under contract for CMMC certification now, you can get in the queue before other organizations rush to meet the compliance deadline. It can take up to 12 months for contractors to get ready for a CMMC assessment. In other words, once CMMC shows up in contract requirements, it will be too late to get started.
Given the large number of organizations (roughly 80,000) that will need certification and the fact that there are less than 85 C3PAOs that can perform assessments, organizations that don’t get ahead could get left behind.
Don’t wait — get ready for CMMC 2.0 now with A-LIGN
If you’re ready to take the next step toward CMMC compliance, contact us today. The A-LIGN difference is:
- Deep federal expertise with 1,000 federal assessments completed and more than 50 federal global staff.
- A quick start to CMMC with a kickoff in just 6-8 weeks alongside our experienced federal team. The industry average is 2x this timeline.
- Scalable support to be ready even while other C3PAOs get inundated.
Don’t get left behind. Reach out today to learn how A-LIGN can help you navigate this next step in your compliance journey.





