The European Union is raising its bar for compliance with the roll out of NIS2, but what exactly is it and how can companies ensure they comply? We’re here to break down this regulation and share the best way for organizations to achieve compliance by following the ISO/IEC 27001:2022 framework.
What is NIS2?
Replacing the original NIS Directive, NIS2 sets out to redefine minimum security requirements for operators of essential services and digital service providers. This update drives broader applicability across more industries, introduces new methods for onboarding companies, establishes stricter requirements for reporting incidents, and enforces harsher penalties for non-compliance. It’s intended to strengthen cybersecurity in the EU, ensuring all companies in the scope of the NIS2 directive that provide services or carry out activities within the EU take proactive measures to create a more secure operating environment.
Check out our article NIS2 Directive: What You Need to Know to take a deeper dive into the updates and requirements for this regulation.
What is ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 is an internationally recognized standard that focuses on the implementation, management, and maintenance of information security within a company. It’s a powerful framework for governance because it gives organizations flexibility to ensure that what they’re implementing aligns with their business goals. It builds a strong foundation for security practices, focusing not just on controls but on a robust management system.
To learn more about ISO 27001, check out our article ISO 27001 Certification: Everything You Need to Know
Using ISO 27001 as a tool for NIS2 compliance
The NIS2 Directive does not provide a clear roadmap for how to achieve compliance, which leaves many organizations wondering how they can meet the guidelines of the directive and avoid penalties for non-compliance. While ISO 27001 is not specifically mentioned, the directive does allude to “relevant European and international standards.” Our team of experts at A-LIGN believe that NIS2 compliance can be achieved with the ISO 27001 framework, incorporating additional requirements for business continuity and incident management.
Mapping the Overlap
There are ten minimum security measures for NIS2 that build on and align closely with ISO 27001, adding specific business continuity requirements to enhance organizational resilience. Certifying against ISO 27001 and mapping to NIS2 controls demonstrates conformity of your Information Security Management System (ISMS) with the documented standards and provides your customers with assurance regarding the security of your systems and data. If you are already ISO 27001 compliant, mapping to NIS2 controls enhances compliance by aligning with EU-specific requirements and emphasizes incident reporting. It also gives you a competitive edge by demonstrating a robust commitment to cybersecurity.
NIS 2 article
ISO 27001 clause or control
Article 21.2 a) Policies on risk analysis and information system security
- 5.2 Policy
- 6.1.2 Information security risk assessment
- 6.1.3 Information security risk treatment
- 8.2 Information security risk assessment
- 8.3 information security risk treatment
- A.5.1 Policies for information security
Article 21.2 b) Incident handling
- A.5.24 Information security incident management planning and preparation
- A.5.25 Assessments and decision on information security events
- 5.26 Response to information security incidents
- 5.27 Learning from information security incidents
- 5.28 Collection of evidence
- 6.8 Information security event reporting
Article 21.2 c) Business continuity, such as backup management and disaster recovery, and crisis management
- A.5.29 Information security during disruption
- A.5.30 ICT readiness for business continuity
- 8.13 Information backup
- 8.14 Redundancy of information processing facilities
Article 21.2 d) Supply chain security, including security-related aspects concerning the relationship between each entity and its direct suppliers or service providers
- A.5.19 Information security in supplier relationships
- A.5.20 Addressing information security within supplier agreements
- A.5.21 Managing information security in the ICT supply chain
- A.5.22 Monitoring, review and change management of supplier services
- A.5.23 Information security for use of cloud services
Article 21.2 e) Security in network and information systems acquisition, development and maintenance, including vulnerability handling and disclosure
- A.5.37 Documented operating procedures
- A.8.8 Management of technical vulnerabilities
- A.8.9 Configuration management
- A.8.20 Network Security
- A.8.21 Security of network services
Article 21.2 f) Policies and procedures to assess the effectiveness of cybersecurity risk management measures
- 9.1 Monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation
- 9.2 Internal audit
- 9.3 Management review
- A.5.35 Independent review of information security
Article 21.2 g) Basic computer hygiene practices and cybersecurity training
- 7.3 Awareness
- 7.4 Communication
- A.6.3 Information security awareness, education and training
Article 21.2 i) Human resources security, access control policies and asset management
- A.6.1 Screening
- A.6.2 Terms and conditions of employment
- A.6.4 Disciplinary process
- A.6.5 Responsibilities after termination or change of employment
- A.6.6 Confidentiality or non-disclosure agreements
- A.5.15 Access control
- A.5.16 Identity Management
- A.5.17 Authentication information
- A.5.18 Access Rights
- A.5.9 Inventory of information and other associated assets
- A.5.10 Acceptable use of information and other associates assets
Article 21.2 j) The use of multifactor authentication or continuous authentication solutions, secured voice, video, and text communications and emergency communication systems within the entity, where appropriate
- A.5.16 Identity Management
- A.5.17 Authentication information
- A.5.14 Information transfer
- ◆A.5.16 Identity Management
- ◆A.5.17 Authentication information
- ◆A.5.18 Access Rights
- ◆A.5.9 Inventory of information and other associated assets
- ◆A.5.10 Acceptable use of information and other associates assets
A-LIGN is at the forefront of ISO 27001 certification and has a team of experts ready to help you navigate the audit process and achieve compliance. Reach out to us today to get started with ISO 27001 certification for 2025.
The European Union Artificial Intelligence Act (EU AI Act) has established a comprehensive framework for regulating AI, setting a precedent for global AI governance. As enforcement phases roll out, organizations must proactively implement compliance measures to avoid legal and operational risks. However, due to evolving regulatory interpretations and industry-specific obligations, many organizations face uncertainty regarding compliance strategies.
ISO/IEC 42001, the AI Management System (AIMS) standard, provides a structured, risk-based approach to AI governance that aligns with the EU AI Act’s requirements. This article outlines the regulatory timeline and demonstrates how companies can leverage ISO 42001 to systematically prepare for compliance.
What is the EU AI Act?
The EU AI Act is a groundbreaking legislative proposal designed to regulate artificial intelligence across the European Union. Its core objective is to establish a legal framework that balances technological innovation with the protection of fundamental rights and public safety. The act classifies AI applications into four risk categories: unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal, each subject to specific rules or restrictions.
What is ISO 42001?
ISO 42001 is an international standard dedicated to establishing effective artificial intelligence management systems. This standard outlines a structured framework that organizations can adopt to ensure the responsible and ethical use of AI technologies.
Published on December 18, 2023, this standard provides guidance to organizations that design, develop, and deploy AI systems on factors such as transparency, accountability, bias identification and mitigation, safety, and privacy.
EU AI Act timeline
The EU AI Act became legally binding on August 1, 2024. However, the requirements in the act will begin to take effect gradually over time with a phased roll out. Key milestones include:
- February 2, 2025: Prohibitions on certain AI systems and requirements on AI literacy start to apply.
- August 2, 2025: Rules start to apply for notified bodies, GPAI models, governance, confidentiality and penalties.
- August 2, 2026: The remainder of the AI Act starts to apply, except for some high-risk AI systems with specific qualifications.
- August 2, 2027: All systems, without exception, must meet obligations of the AI Act.
February 2025 milestones
The first major enforcement deadline—February 2, 2025—introduced two key requirements:
- Prohibited AI practices: The Act explicitly bans AI systems that engage in manipulative behavior, social scoring, or unauthorized biometric surveillance. Organizations that have not conducted internal risk assessments to identify and eliminate these practices are already non-compliant.
- AI literacy requirements: Organizations must ensure that employees involved in AI decision-making possess adequate training in AI risk management, explainability, and governance. This requirement applies to developers, compliance teams, and executives responsible for AI oversight.
Organizations that have not yet implemented structured compliance mechanisms must act immediately, as future enforcement deadlines impose stricter obligations on AI transparency and risk management.
August 2025 milestones
The next major deadline introduces requirements for general-purpose AI (GPAI) providers, including foundational models and large-scale AI systems.
- Transparency disclosures: AI providers must publicly disclose details about model training methodologies, datasets, and inherent risks.
- Explainability and accountability: Organizations must ensure AI outputs are understandable, predictable, and governed by clearly defined policies.
ISO 42001 provides a structured approach to meeting these requirements:
- Clause 7.4 (Communication & transparency) outlines best practices for documenting and disclosing AI models and decision-making processes.
- Clause 6.1.3 (AI system impact assessment) supports organizations in evaluating AI bias, ethical risks, and explainability, reinforcing compliance with EU AI Act transparency mandates.
For companies developing GPAI models, establishing robust transparency mechanisms is essential to avoid regulatory penalties.
August 2026 milestones
By this date, high-risk AI systems defined in Annex III of the EU AI Act must fully comply with strict legal, technical, and governance requirements. These systems are deployed in sectors such as healthcare, critical infrastructure, law enforcement, and human resource management.
Organizations must ensure high-risk AI systems:
- Implement rigorous risk management practices
- Include bias detection and mitigation controls
- Maintain security and explainability safeguards
ISO 42001 establishes a structured risk-management framework that directly aligns with high-risk AI system compliance:
- Clause 8.2 (AI risk treatment) enables organizations to systematically identify, assess, and mitigate AI risks.
- Clause 9 (Performance evaluation) mandates ongoing risk monitoring, bias audits, and transparency reporting, ensuring continued compliance.
Organizations operating high-risk AI must implement structured AI governance frameworks to meet this compliance milestone.
August 2027 milestones
Certain high-risk AI systems integrated into pre-existing EU-regulated industries (e.g., medical devices, finance, and automotive) will be subject to an extended compliance timeline. AI systems requiring pre-market conformity assessments under sector-specific EU laws must meet full AI Act compliance by this date.
ISO 42001 facilitates multi-standard compliance and audit readiness:
- ISO 42001 integrates with ISO 27001 (Information Security) and ISO 13485 (Medical Devices), providing a unified compliance framework.
- ISO 42001 supports AI conformity assessments, positioning organizations for third-party regulatory audits.
Organizations in regulated industries should begin integrating AI governance structures now to ensure seamless compliance by 2027.
Why ISO 42001 is essential for EU AI Act compliance
The EU AI Act mandates an ongoing governance framework for AI risk management, transparency, and compliance. Unlike one-time risk assessments or ad hoc governance policies, ISO 42001 establishes a systematic, repeatable process for AI compliance, ensuring organizations:
- Proactively manage AI risks rather than responding to enforcement actions.
- Align AI governance with business operations using structured risk-management frameworks.
- Demonstrate compliance through audit-ready documentation and performance evaluation.
ISO 42001 provides an adaptable compliance framework that evolves alongside regulatory requirements, making it an ideal foundation for AI governance. Though it is not an approved harmonized standard for AI Act conformity, it does provide the foundation you’ll need to be successful when the final QMS conformity standard is released.
Recommendations for EU AI Act compliance
Organizations should take the following steps to ensure readiness for EU AI Act enforcement:
- Conduct an AI risk & readiness assessment: Map AI systems to EU AI Act categories and use ISO 42001’s risk framework to identify compliance gaps.
- Implement AI literacy programs: Ensure personnel meet EU AI Act training requirements through structured education initiatives outlined in ISO 42001 Clause 7.2 (Competence).
- Develop AI governance policies: Use ISO 42001 to define roles, responsibilities, and oversight mechanisms for AI compliance.
- Prepare for independent audits: ISO 42001 provides an audit-ready AI governance structure, ensuring organizations are prepared for third-party conformity assessments.
The EU AI Act is now law, and enforcement will intensify over the next two years. Organizations that wait until 2026 or 2027 to implement compliance measures will face significant operational and regulatory risks. ISO 42001 provides a structured, proactive approach to AI governance, ensuring that organizations remain compliant, transparent, and resilient in a rapidly evolving regulatory landscape.
The question is no longer whether AI governance will become mandatory—it already is. The real challenge is ensuring that organizations implement compliance structures that are sustainable, scalable, and aligned with industry best practices. Organizations that take action now will be best positioned to thrive in the new AI regulatory environment.
With bad actors targeting sensitive data, many organizations are looking for new ways to monitor and improve their data security — Enter: ISO/IEC 27001:2022. Earning your ISO 27001 certification is a useful way to establish credibility with stakeholders, customers, and partners, and in turn, helps demonstrate your organization’s commitment to cybersecurity.
Of course, like most standards, the certification process can seem daunting at first glance. Here’s what you need to know before your organization decides to pursue an ISO 27001 certification.
What is ISO 27001?
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) originally published ISO 27001 in October 2005, revised in 2013, and again in 2022. It focuses on building a strong information security management system (ISMS) within organizations.
As one of the most widely used security frameworks around the world, ISO 27001 is a risk-driven standard that focuses on data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. The standard aims to help organizations have a stronger, more holistic approach to data security.
What are the benefits of ISO 27001 certification?
- Defines responsibilities and business processes for information security
- Builds a culture of information security and diligence
- Reduces the potential for security incidents through implemented controls specific to your unique risks and assets
- Meets additional security compliance requirements
Who should get a certification for ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 isn’t a legal requirement but may be a prerequisite to customers doing business with your organization.
Some industries are more likely to need an ISO 27001 certification because of the type of data that companies store. These industries include:
- Information technology
- Healthcare
- Finance
- Consulting
- Telecommunications
What is the difference between ISO 27001 and SOC 2?
ISO 27001 and SOC 2 are two of the most popular cybersecurity assessments that verify an organization’s ability to mitigate risk and protect information. However, the two standards are not interchangeable.
SOC, or System and Organizational Controls, is a framework developed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) with the aim of providing regular, independent attestation of the controls that an organization has implemented to mitigate information-related risk. There are three types of SOC audits: SOC 1, SOC 2, and SOC 3, although SOC 2 has become the de facto standard for cybersecurity.
Difference #1: Certification vs. attestation
The biggest difference between ISO 27001 and SOC 2 is that ISO 27001 is an audit process that results in a certification, and SOC 2 is an audit process that results in an attestation report. In an attestation report, a third-party assessor documents a conclusion about the reliability of a written statement over a prior time period. ISO 27001 certifications, on the other hand, are issued by an accredited certification body or the International Accreditation Forum (IAF) seal and lasts for 3 years.
Difference #2: Global reach
ISO 27001 is an international standard that is used as the principal cybersecurity standard throughout the world. SOC 2 is an American-born standard, and although it is gaining popularity in Europe, it has yet to have the same global reach as ISO 27001.
Difference #3: ISMS vs. Trust Service Criteria (TSC)
ISO 27001 focuses on the development and maintenance of an Information Security Management System (ISMS). In order to earn an ISO 27001 certification, organizations must implement all of the clauses and controls of the framework within the scope of its ISMS. The organization will then be issued a pass or fail of the audit. Organizations would need to implement, maintain and continually improve the ISMS in order to achieve an ISO 27001 certification.
SOC 2 is structured around five Trust Services Criteria (TSC): Security, Availability, Confidentiality, Processing Integrity, and Privacy. For a SOC 2 audit, organizations can mostly pick which criteria they’d like to have evaluated (Security is mandatory). The final report is not pass/fail but rather the auditor concludes an opinion based on the design and effectiveness of the operation of controls in place for each chosen TSC.
Difference #4: Certification bodies and renewal timelines
For SOC 2, the attestation is carried out by a licensed CPA firm. ISO 27001 certifications must be carried out by an accredited ISO 27001 certification body.
How do ISO 27001 and ISO 42001 overlap?
ISO 27001 provides a great foundation for ISO 42001, a new standard for AI use. But, the two are not the same. Here’s how they differ:
- Scope: ISO 27001 focuses on ISMS and provides a framework to protect sensitive information through risk management processes. ISO 42001, however, deals with AI management systems. This standard includes responsibilities specific to AI, such as ethical considerations and impact assessments.
- Normative references: ISO 27001 references various information security management standards. These guidelines help organizations maintain data integrity, confidentiality, and availability. ISO 42001 incorporates AI-specific standards, like ISO/IEC 22989. These references focus on ethical AI use, risk management, and system integrity.
- Context of the organization: ISO 27001 requires organizations to understand the context of their information security needs. ISO 42001 extends this concept to AI. Organizations must understand the specific context of their AI systems, including stakeholder expectations and potential impacts. ISO 42001 also requires organizations to understand their role in the AI ecosystem as provider, producer, or user.
Understanding the overlaps and differences between these two frameworks can streamline your compliance efforts and keep your team ahead of the curve. Learn more about ISO 42001 vs. ISO 27001.
Preparing for your ISO 27001 audit
The prep work is just as important as the audit when it comes to compliance. Your organization should take the time to understand the standard, define your goals, and research accredited certification bodies, or organizations. You should also consider conducting a gap assessment and understand the state of your company’s compliance journey before jumping into an ISO 27001 audit.
Steps to ISO 27001
While the road to ISO 27001 certification is well-established, it is still a multi-pronged process that requires attention to detail and a generous time commitment. The five steps to ISO 27001 certification include:
- Optional Pre-Assessment
- The Stage 1 Audit
- The Stage 2 Audit
- A Surveillance Audit
- Recertification
In order to make the ISO 27001 certification process as smooth as possible, A-LIGN offers end-to-end services, from pre-assessment to ongoing audits to recertification. Our experts ensure your organization can continue to run with minimal disruption while still helping you acquire the certification you need to strengthen your security.
Step 1: Pre-assessment
The pre-assessment is designed for companies that are undergoing the certification process for the first time. This assessment is only performed on an as-needed basis but is highly recommended prior to the actual audit.
The pre-assessment involves performing a review of an organization’s scope, policies, procedures, and processes to review any gaps in conformance that may need remediation before the actual certification process begins.
Step 2: Stage 1 audit
During a Stage 1 audit, an auditor reviews an organization’s ISMS to confirm that it has been established and implemented in conformance with the ISO 27001 standard. This audit also checks to see if the mandatory activities of an ISMS have either been completed prior to starting Stage 2.
Upon completion, the Stage 1 audit will reveal if an organization is ready to move forward to Stage 2 or if it needs to modify its policies, procedures, and supporting documentation before proceeding.
Step 3: Stage 2 audit
The Stage 2 audit tests the conformance of an organization’s ISMS against the ISO 27001 standard. Upon completion of Stage 2, A-LIGN will determine if an organization is ready for certification.
If any nonconformities were identified during the audit, they will need to be remediated by the organization before a certificate can be issued.
Stage 4: Surveillance audit
The ISO 27001 certification process doesn’t simply end after a certificate has been issued. For the two years following certification, A-LIGN will conduct annual surveillance audits to ensure an organization’s ongoing compliance with the ISO 27001 standards. This step ensures your cybersecurity practices are operating at the highest possible level.
Stage 5: Recertification
An ISO 27001 certification is valid for three years after the certificate’s issue date. Organizations need to recertify before the certificate’s expiration date or be required to begin the certification process again. Recertification audits review the entire management system, similar to the Stage 2 audit.
How do I choose an assessor?
Once an organization decides to pursue an ISO 27001 certification, they must then decide which path to take toward certification. This initial step in the process means choosing a certification body (CB).
A CB is an organization that provides certifications around a chosen standard. These organizations come in two forms: accredited and unaccredited.
Although the process taken by both accredited and unaccredited certification bodies are similar, there are enough differences to consider the risks that come from using unaccredited certification bodies before they begin pursuing ISO 27001 certification.
Accredited certification bodies
Accredited certification bodies must complete a rigorous evaluation process through an accreditation body. This is done to ensure the certification audit it conducts is performed in accordance with the audit requirements.
The evaluation process involves reviewing the competence of the audit team, the audit methodology used by the certification body, and the quality control procedures an organization has in place to ensure the audit and certificate are performed/issued accurately.
Organizations that use an accredited certification body for certification will receive their ISO 27001 certifications with the accreditation body represented on the certificate. Additionally, for certification bodies that have entered into the IAF Multilateral Recognition Arrangement (MLA) under their accreditation body, the IAF MLA mark will appear on the certificate as well in addition to the AB’s mark. Accreditation granted by the IAF MLA are recognized globally for equivalent programs and recognize acceptance of certificates across global markets. Accreditation bodies are admitted to the MLA after a peer review, and their certification bodies are held to auditable requirements. Recognized accreditation bodies and scopes can be verified on the IAF website.
Unaccredited certification bodies
Because accreditation is not compulsory, non-accreditation does not always mean the certification body is not reputable. Accreditation, however, does provide a confirmation that the certification body is approved. An unaccredited certification body is not audited to confirm their compliance with IAF certification audit requirements.
Oftentimes clients will only accept ISO 27001 certificates from accredited certification bodies. It is important for organizations to check if their clients have any specific accreditation requirements before they begin their certification process.
Common pitfalls
All certification processes come with the chance of not getting approved for certification, and ISO 27001 is no exception. Here are some of the most common ISO 27001 pitfalls organizations make, along with how you can avoid making the same missteps.
Pitfall #1: Failing to schedule the internal audit and management review
Both the internal audit and management review are critical to the success of the ISMS, as the internal audit feeds into the management review, and then both feed into the continuous improvement cycle.
However, the certification process can be easily disrupted if the internal audit and management review are not scheduled within the proper time frame. Organizations should make sure their internal audit is scheduled well in advance of the certification audits in order for management review and continuous improvement activities to have enough time to be completed. The internal audit and management review of the ISMS must be completed prior to the Stage 2 audit.
A-LIGN starts the surveillance audit approximately nine months after receiving initial certification. This means an organization would start the next internal audit six to seven months after certification.
Pitfall #2: Changes in key personnel
Most times, the ISMS is implemented by someone who fields many of the questions during an audit, taking overall responsibility for the ISMS. If this person leaves their role, the ISMS can fall apart.
Organizations need to ensure they have a redundant person who has a basic understanding of the ISMS. Even if this person never has to step up and take over the process, having an established transition process ahead of time can alleviate any potential headaches down the line. Detailed documentation will be key to this transition and will help ensure the new ISMS Manager can continue carrying out the processes required.
Pitfall #3: Failing to be vigilant
ISO 27001 defines ongoing processes that should be in place throughout the year, not just during the audit itself. Management controls, which include periodic meetings, documented approvals for decisions, recording meeting minutes of oversight committees, etc., require maintenance for the ISMS to continue to function.
It is easy to fall into a period of false security and let oversight slip. Organizations should make sure their ISMS is a living process that is built into their day-to-day so that it continues to function as designed after certification is received.
Pitfall #4: Not considering environmental changes
ISO 27001 requires that all changes in the environment must be considered through the risk assessment process. It also requires new or modified controls to be mentioned in the statement of applicability.
The certification body you choose must also be notified and a new certificate issued if there are changes to the scope or statement of applicability.
When changes in the environment may impact the scope of certification, it is necessary to review and update the ISMS documentation to ensure it correctly reflects the environment post-change.
What is ISO 27701?
Acting as an extension of ISO 27001, ISO 27701 is the first international privacy standard to provide a certification path for organizations to demonstrate their privacy systems and controls.
The ISO/IEC 27701:2019 standard was first published in 2019. It details the requirements and guidance for establishing, implementing, maintaining and continually improving a Privacy Information Management System (PIMS). Although this standard is most relevant for personally identifiable information (PII) controllers and processors, it can also be used by organizations of any kind, size, and location. An important thing to remember is that most organizations are at the very least a controller of their employees’ data.
To receive an ISO 27701 accredited certificate, organizations must either already have ISO 27001 certification or must undergo the ISO 27001 certification audit with the extension of ISO 27701.
Why organizations may want to pursue ISO 27001 and ISO 27701
Outside of simply gaining a better understanding of the PIMS implementation process, there are multiple benefits that come from pursuing ISO 27701 and ISO 27001. Combining the two certifications:
Streamlines compliance obligations for ISO 27001 and the GDPR by integrating privacy directly into an organization’s ISMS
Helps organizations surpass the competition and attract new customers by adding a level of increased security and privacy into the organization
Maintains peace of mind for current customers as they know their personal identifiable information (PII) is protected
Helps organizations avoid potential fines, especially as the enforcement of privacy protection continues to increase
The underlying, foundational framework of ISO 27001 creates a strong ISMS. Alongside the ongoing PIMS improvement structure of ISO 27701, organizations can benefit from combining the two and ensuring a certifiable commitment to privacy controls.
A-LIGN recognizes the complex compliance needs for businesses that require cybersecurity compliance assessments in the U.S. and EMEA region. To cater to this growing demand, A-LIGN has successfully pursued and obtained accreditation from both ANAB and UKAS specifically to the ISO 27001 and ISO 27701 standards.
What are the ISO 27001 controls and requirements?
What are the ISO 27001 controls and requirements?
The ISO 27001 requirements provide a clear framework for protecting and managing valuable data and information. In the 2013 version of ISO 27001, controls were organized into 14 different domains. In the 2022 update, controls are placed into four themes instead:
People controls (8 controls)
Organizational controls (37 controls)
Technological controls (34 controls)
Physical controls (14 controls)
Below is a summary of the new controls in ISO Annex A:
A.5.7 Threat Intelligence: This control requires organizations to gather and analyze information about threats, so they can take action to mitigate risk.
A.5.23 Information Security for Use of Cloud Services: This control emphasizes the need for better information security in the cloud and requires organizations to set security standards for cloud services and have processes and procedures specifically for cloud services.
A.5.30 ICT Readiness for Business Continuity: This control requires organizations to ensure information and communication technology can be recovered/used when disruptions occur.
A.7.4 Physical Security Monitoring: This control requires organizations to monitor sensitive physical areas (data centers, production facilities, etc.) to ensure only authorized people can access them — so the organization is aware in the event of a breach.
A.8.9 Configuration Management: This control requires an organization to manage the configuration of its technology, to ensure it remains secure, and to avoid unauthorized changes.
A.8.10 Information Deletion: This control requires the deletion of data when it’s no longer required, to avoid leaks of sensitive information, and to comply with privacy requirements.
A.8.11 Data Masking: This control requires organizations to use data masking in accordance with the organization’s access control policy to protect sensitive information.
A.8.12 Data Leakage Prevention: This control requires organizations to implement measures to prevent data leakage and disclosure of sensitive information from systems, networks, and other devices.
A.8.16 Monitoring Activities: This control requires organizations to monitor systems for unusual activities and implement appropriate incident response procedures.
A.8.23 Web Filtering: This control requires organizations to manage which websites users access, to protect IT systems.
A.8.28 Secure Coding: This control requires secure coding principles to be established within an organization’s software development process to reduce security vulnerabilities.
How does ISO 27001 relate to GDPR compliance?
Achieving ISO 27001 certification can cover many aspects of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) but it’s impossible to fully swap a standard and a regulation. While ISO 27001 does not equal GDPR compliance, it’s a great starting point.
How long is ISO 27001 certification valid?
ISO 27001 certifications are valid for a three-year period with annual surveillance audits.
What’s an example of ISO 27001 in the real world?
Below are customer case studies in which the organization earned ISO 27001 certification to drive revenue, build customer trust, and better their security posture.
Magic achieves SOC 2, ISO 27001, and HIPAA compliance with A-LIGN & Drata
Anthology’s commitment to compliance elevates edtech standards
Boomi showcases cybersecurity dedication with 10+ compliance certifications and attestations
Menlo Security reduces evidence collection time by 60% with consolidated audit approach
Getting started with ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is a longstanding cybersecurity framework used to build an ISMS within your organization. This internationally recognized framework is a risk-driven standard focusing on the confidentiality, integrity and availability of the data in your environment.
As an accredited ISO 27001 certification body, A-LIGN can provide your organization with the experience and guidance needed to achieve certification. Contact us to get started today.
If your company is a prime or subprime contractor for the Department of Defense (DoD), you should be familiar with CMMC. That’s because CMMC requirements are now included in all new DoD solicitations and contracts because of the 48 CFR rule.
What does that mean for your business, and how should you prepare? In this post, we cover everything you need to know about CMMC.
What is CMMC 2.0?
The first question many people have is, “What does CMMC stand for?” CMMC stands for Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification. CMMC is designed to ensure that cybersecurity controls and processes adequately protect Federal Contract Information (FCI) and Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) that resides on Defense Industrial Base (DIB) systems and networks.
CMMC 1.0 was finalized in 2020. CMMC 2.0 — published in October 2024 — is an updated framework with three control levels, as opposed to the five maturity levels in CMMC 1.0.
What is a C3PAO?
A C3PAO is a CMMC Third Party Assessment Organization, The Cyber AB authorizes a C3PAO to contract and manage CMMC assessments and only authorized C3PAOs can conduct CMMC assessments.
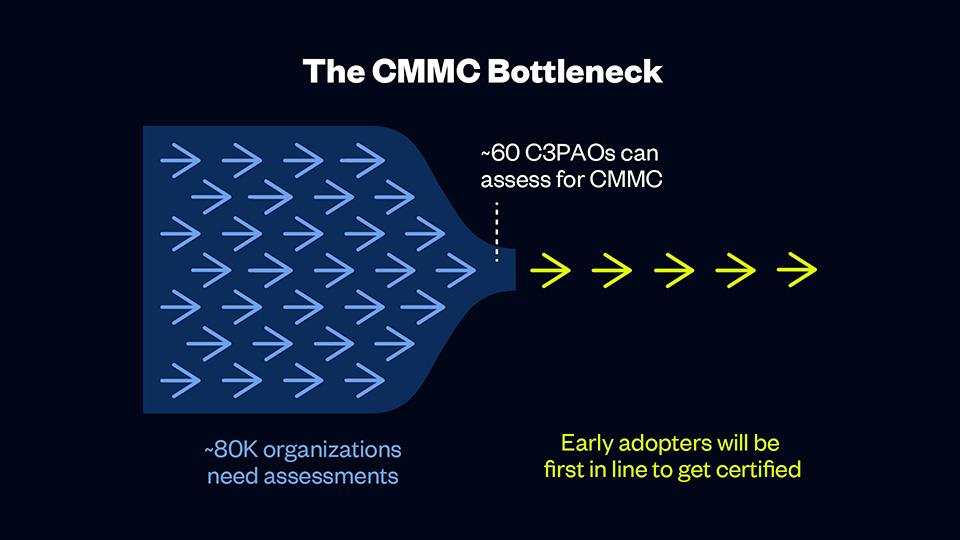
Currently, fewer than 85 C3PAOs can assess for CMMC, and more than 80,000 organizations need assessments. That means early adopters will have their pick of C3PAOs and will be first in line to receive certification, and organizations who are slow to act may face long waitlists or delays.
A C3PAO is an essential partner in your CMMC journey. C3PAOs follow the CMMC assessment process and conduct thorough assessments of DoD contractors. Although the Cyber AB authorizes all C3PAOs, each organization has different strengths and weaknesses, so you must choose an organization that meets your needs. Get a checklist of questions to ask a C3PAO in our CMMC Buyer’s Guide to ensure you’re choosing the right partner for your CMMC journey.
CMMC 2.0 requirements
With the CMMC 2.0 program, the DoD introduced several changes compared to the original version of the program. Most obviously, the model has been streamlined from five to three compliance levels that each correspond with existing, widely accepted cybersecurity standards. And while many organizations will require third-party assessment, many will be able to demonstrate compliance through self-assessment, reducing costs for these organizations. Additionally, the DoD will allow companies to receive contract awards with the creation of a Plan of Action & Milestones (POA&M) that describes how and when CMMC controls will be met.
The CMMC 2.0 model
The CMMC 2.0 framework organizes multiple cybersecurity standards and best practices into a set of practices and processes across three increasingly stringent levels. These practices and processes must be applied across 14 domains (i.e., control families):
- Access Control (AC)
- Awareness & Training (AT)
- Audit & Accountability (AU)
- Configuration Management (CM)
- Identification & Authentication (IA)
- Incident Response (IR)
- Maintenance (MA)
- Media Protection (MP)
- Personnel Security (PS)
- Physical Protection (PE)
- Risk Assessment (RA)
- Security Assessment (CA)
- System and Communications Protection (SC)
- System and Information Integrity (SI)
What are the levels of CMMC 2.0?
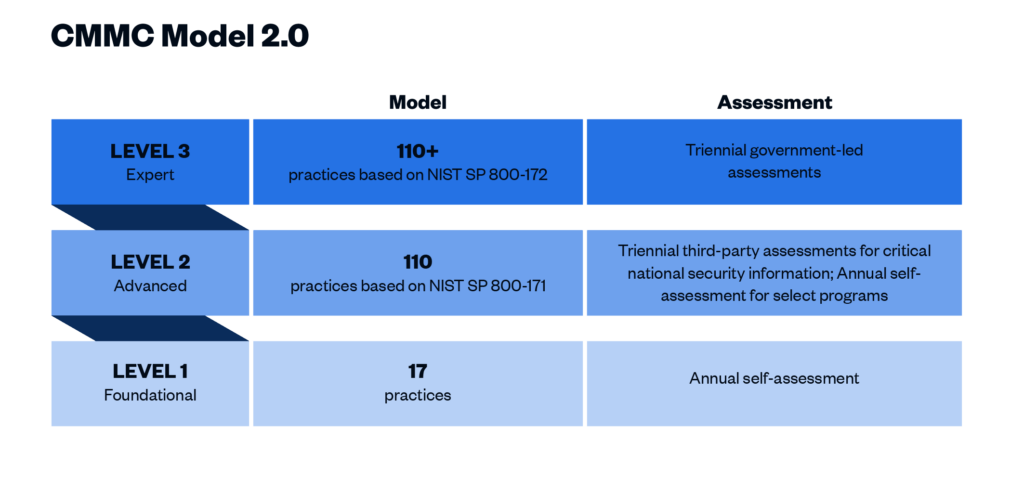
CMMC 2.0 Level 1 (“Foundational”) requirements
This level includes basic cybersecurity appropriate for small companies using a subset of universally accepted common practices that organizations must perform. Level 1 contractors are those that handle Federal Contract Information (FCI) but not CUI. One of the more significant changes from CMMC 1.0 to 2.0 is that Level 1 is now a self-assessment only, placing this responsibility on the organization itself. Level 1 includes the same 15 controls outlined in Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) 52.204-21.
CMMC 2.0 Level 2 (“Advanced”) requirements
Level 2 contractors are those that handle CUI. Processes at this level are maintained and followed, and there is a comprehensive knowledge of cyber assets. The DoD has pared down the 130 practices in the original CMMC Level 3 baseline to the 110 practices outlined in the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication 800-171. “Critical” handlers of CUI will need a third-party assessment by a CMMC Third Party Assessment Organization (C3PAO) for CMMC certification every three years. Level 2 processes must be documented and managed to protect CUI.
Note: The DoD’s definition of “critical” CUI has not yet been provided. The final rule will outline what CUI qualifies as critical.
CMMC 2.0 Level 3 (“Expert”) requirements
Level 3 is for organizations with the highest-priority programs with CUI. The processes involved at this level include continuous improvement across the enterprise and defensive responses performed at machine speed. This level will replace what was formally known as CMMC Level 5. Level 3 will add additional requirements pulled from NIST 800-172 in addition to the Level 2 requirements. It is expected that organizations will be required to be assessed by the DoD directly every three years for Level 3 requirements.
CMMC 2.0 vs. NIST 800-171
CMMC 2.0 is influenced heavily by the requirements in NIST 800-171. CMMC 2.0 Level 2 essentially mirrors NIST 800-171. If your organization processes CUI and does business with the DoD, you are already required to implement NIST 800-171 under Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement (DFARS) Clause 252.204-7012.
Additionally, the DFARS Interim Rule went into effect in November 2020. The interim rule requires DoD contractors to self-assess their implementation of NIST 800-171 and report their score through the Supplier Performance Risk System (SPRS). Performing this self-assessment and remediating any identified gaps simulates what CMMC 2.0 certification will be like.
What is 48 CFR?
The CMMC 48 CFR is the final rule and that makes CMMC enforceable in DoD contracts. The rule was published in the Federal Register on September 10, 2025 with an effective date of November 10, 2025. This marks the official start of Phase 1 of the CMMC roll out, meaning readiness is no longer optional and all new DoD solicitations and contracts include some level of CMMC requirement.
Who must comply with CMMC?
CMMC 2.0 is now mandatory for all entities doing business with the DoD at any level who store, transmit, or process information that meets the standards for FCI or CUI. Prime contractors and their subcontractors are required to meet one of the three CMMC trust levels and demonstrate that cybersecurity has been sufficiently implemented through the completion of independent validation activities. Initial award or continuance of a DoD contract will be dependent upon CMMC compliance.
No contractor organizations will be permitted to receive or share DoD information related to programs and projects without having completed the CMMC process. At the time that a contractor’s contract is up for renewal, they must be CMMC compliant.
CMMC 2.0 timeline
The Office of the Undersecretary of Defense for Acquisition and Sustainment (OUSD (A&S)) started the CMMC process in March 2019. The predicted date for the CMMC 2.0 rulemaking process to be completed has shifted several times, but the timeline below provides a history of significant milestones in the project thus far.
- January 2020: Version 1.0 was finalized and a compliance checklist was released.
- June 2020: CMMC began appearing in requests for information (RFIs).
- September 2020: CMMC began appearing in requests for proposals (RFPs).
- November 2020: The DFARS interim rule became effective; the original five-year phase-in period began.
- March 2021: DoD initiated an internal review of CMMC 1.0.
- November 2021: CMMC 2.0 was announced.
- September 2022: Cyber AB, the CMMC accreditation body, established training and accreditation processes.
- December 2023: The CMMC program proposed rule was released.
- May 2024: DoD’s Regulatory Control Officer submitted a draft of the proposed DFARS rule to the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs (OIRA).
- June 2024: 32 CFR 170, the rule finalizing the CMMC program, was submitted to OIRA for review.
- August 2024: The proposed rule for 48 CFR, the rule implementing the enforcement of the CMMC program into contract requirements was released.
- October 2024: 32 CFR, the rule finalizing the CMMC 2.0 program, was published.
- September 2025: 48 CFR, the rule that makes CMMC enforceable in CMMC contracts, is published in the Federal Register.
- November 2025: 48 CFR goes into effect, meaning readiness is no longer optional and all new DoD solicitations and contracts include some level of CMMC requirement.
Has CMMC 2.0 been released?
The 32 CFR final rule was published in October 2024.
When will CMMC 2.0 certifications be available?
To obtain a CMMC Level 2 Certification, you will need to be assessed by a C3PAO. Assessments are now underway as 48 CFR has made readiness mandatory.
How much does CMMC certification cost?
CMMC assessment costs are very scope-dependent as different organizations will have different sensitive data flowing through different numbers of assets. The DoD has assumed for the phased rollout of CMMC that roughly 35% of DIB contractors will require a certification assessment for Level 2, with the number of entities increasing incrementally over seven years (see p. 89085-89086 of Federal Register Vol. 88, No. 246).
With that said, the potential loss in business is too large for most organizations to forego certification. As mentioned earlier in this article, CMMC compliance is now required for all DoD prime and subprime contractors. For contractors that fall in CMMC Levels 2 and 3 and handle critical CUI, third-party certification is mandatory to continue doing business with the DoD.
Next steps: How to prepare for CMMC 2.0 certification
- Determine your organization’s CMMC level. Level 1 is for contractors and subcontractors processing FCI. Level 2 is for organizations processing CUI. Only organizations working on the DoD’s most sensitive programs will be expected to achieve Level 3 certification.
- Review the assessment guide for your CMMC level. The CMMC Level 1 Self-Assessment Guide and Level 2 Assessment Guide explain how contractors will be evaluated when CMMC is launched and organizations are pursuing certification. Unfortunately, there is not yet an assessment guide for CMMC Level 3.
- Work with a tech-enabled organization to secure your data. Cybersecurity solutions like Summit7, RISCPoint, and PreVeil can help you secure your FCI and CUI to prepare for CMMC compliance.
- Select a C3PAO and complete a readiness assessment. With a limited number of C3PAOs, it is important to start validating your organization’s readiness as soon as possible, as you will need time to remediate any gaps found.
- Sign a contract for CMMC certification ASAP. Once CMMC 2.0 certification starts showing up in DoD contracts, organizations that didn’t plan ahead will be scrambling to find a C3PAO and get in line for assessment.
How to select a C3PAO
Choosing the right C3PAO is crucial for a smooth and successful certification process. These are the key factors to consider when making your selection:
- Expertise: Look for a C3PAO with experience in federal compliance frameworks like FedRAMP, NIST, and StateRAMP to ensure they can guide you effectively through the certification process. You should also consider how long the C3PAO has been in business, the experience of its employees, and its overall knowledge of cybersecurity compliance.
- Quality: High-quality C3PAOs go beyond just checking boxes. They bring extensive experience and a deep understanding of CMMC requirements, which helps identify and address potential compliance issues effectively. They also provide thorough assessments and detailed feedback, helping you improve your cybersecurity posture and maintain compliance.
- Efficiency: Look for a C3PAO that uses technology to streamline the certification process. This will accelerate the process and minimize disruptions. To further increase efficiency, consider a firm who can tackle additional frameworks such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, and more.
- Timing: With 48 CFR’s effective date of November 10, 2025, it’s crucial to prepare now. Since this is a new rule, most organizations will need about 6-12 months of preparation before the assessment begins. Make sure your C3PAO can accommodate your timeline and place you in the assessment queue quickly.
- Budget: As with most things, you get what you pay for. Beware of budget C3PAOs that are offering assessments for under-market value. Balance your budget with other important factors listed above like quality, efficiency, timing, and expertise.
Why sign a CMMC certification contract now?
By getting under contract for CMMC certification now, you can get in the queue before other organizations rush to meet the compliance deadline. It can take up to 12 months for contractors to get ready for a CMMC assessment. In other words, once CMMC shows up in contract requirements, it will be too late to get started.
Given the large number of organizations (roughly 80,000) that will need certification and the fact that there are less than 85 C3PAOs that can perform assessments, organizations that don’t get ahead could get left behind.
Don’t wait — get ready for CMMC 2.0 now with A-LIGN
If you’re ready to take the next step toward CMMC compliance, contact us today. The A-LIGN difference is:
- Deep federal expertise with 1,000 federal assessments completed and more than 50 federal global staff.
- A quick start to CMMC with a kickoff in just 6-8 weeks alongside our experienced federal team. The industry average is 2x this timeline.
- Scalable support to be ready even while other C3PAOs get inundated.
Don’t get left behind. Reach out today to learn how A-LIGN can help you navigate this next step in your compliance journey.
The 2025 HITRUST Trust Report provides a compelling look into the evolving landscape of cybersecurity assurance, with key takeaways that reinforce HITRUST’s role in driving continuous improvement, automation, and AI-driven security strategies. As a HITRUST Assessor Firm, we see this report as a roadmap for where compliance and security assurance are headed—shifting from traditional assessments to continuous, data-driven, and AI-integrated risk management.
1. Continuous assurance is the future
HITRUST’s move toward continuous assurance marks a significant industry shift—one that aligns with growing expectations for real-time compliance visibility. Organizations need proof of security and compliance beyond point-in-time assessments, and HITRUST is leading the charge in bridging this gap.
- Our takeaway: Organizations should prepare now by investing in continuous monitoring capabilities and automation.
2. AI security certification & risk management are here
With AI adoption accelerating, HITRUST’s AI Security Certification and AI Risk Management Assessment set a precedent for establishing trust in AI-driven systems. These frameworks will be essential for organizations deploying AI models in critical operations.
- Our takeaway: Companies should start evaluating their AI security posture today—proactive AI governance will soon become an industry expectation.
3. A data-driven approach to risk management
HITRUST is reinforcing data-backed decision-making in cybersecurity assurance by integrating automated risk intelligence, anomaly detection, and proactive risk assessments in its Automated Assurance Intelligence Engine. This technology is a game-changer for assessment accuracy and efficiency.
- Our takeaway: Organizations should leverage automation not just for compliance, but for better risk insights and faster remediation.
4. Strengthening the value of HITRUST verifications
With 99.41% of HITRUST-certified environments reporting no security breaches, the data confirms that HITRUST assessments drive tangible security improvements. The framework’s quality mechanisms—pre-submission reviews, post-submission validation, and assessor performance monitoring—are setting a higher bar for reliability.
- Our takeaway: HITRUST certifications continue to be a market differentiator, and organizations should leverage them to demonstrate security leadership.
5. Evolving from static to dynamic compliance
The traditional audit cycle is evolving. Compliance must now be adaptive, continuous, and deeply embedded into daily operations. HITRUST’s roadmap aligns with a broader industry shift toward proactive, real-time security assurance.
- Our takeaway: Organizations must rethink their security strategies—compliance should no longer be treated as an annual exercise, but as an ongoing business function.
6. Preparing for HITRUST CSF v12 & future enhancements
HITRUST CSF v12 will bring further alignment with global security frameworks, reinforcing the need for scalable, risk-based controls. The addition of AI assurance support, enhanced assessment reporting, and assessor performance monitoring signals a maturing compliance ecosystem.
- Our takeaway: Businesses should stay ahead of these changes by aligning their security programs with HITRUST’s evolving standards.
Final thought: The next era of cybersecurity assurance
The 2025 HITRUST Trust Report isn’t just an overview of trends, it’s a strategic roadmap for organizations to stay resilient in an era of rapid technological change. As a HITRUST Assessor Firm, we are committed to helping organizations adapt, implement, and lead in this new era of cybersecurity assurance.
Need guidance on how these changes impact your organization? Let’s talk about how to navigate the shift toward continuous assurance, AI security, and proactive risk management. Contact us today to learn how you can get started on your HITRUST journey.
When the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) published a new version of ISO/IEC 27001 in 2022, compliance teams were left wondering: What is the difference between ISO/IEC 27001:2013 and ISO/IEC 27001:2022? As the deadline to transition is quickly approaching, companies need to ensure that the organization’s ISO 27001 certification is updated. Read on to learn the steps your organization should take now to transition to the newest ISO 27001:2022 standard.
What is ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 is the world’s leading information security standard, providing control requirements to create an information security management system (ISMS).
ISO 27001:2022 is a moderate update from the previous version of the standard: ISO 27001:2013. The bulk of changes are related to the Annex controls as the updates focused on revamping and better aligning to industry standards that we see today. The Annex controls have been grouped differently, new Annex controls have been added, and others have been merged or renamed.
Updates to Clauses 4-10
ISO 27001:2022 includes the same number of clauses as ISO 27001:2013, but the text has changed slightly. The changes help align ISO 27001 with other ISO management standards.
Significant changes largely revolve around planning and defining process criteria, as well as monitoring standards. Specifically:
Clause 4.2 Understanding the Needs and Expectations of Interested Parties: A new subclause was added requiring an analysis of which of the interested party requirements are going to be addressed through the ISMS.
Clause 4.4 Information Security Management System: New language was added that requires organizations to identify necessary processes and their interactions within the ISMS. Essentially the ISMS must include the processes underpinning the ISMS, not just the ones specifically called out in the standard.
Clause 6.2 Information Security Objectives and Planning to Achieve Them: Now includes additional guidance on the information security objectives. This gives more clarity about how objectives should be monitored regularly and formally documented.
Clause 6.3 Planning of Changes: This clause was added to set a standard around planning for changes. It states that if changes are needed to the ISMS, they shall be adequately planned for.
Clause 8.1 Operational Planning and Control: Additional guidance was added for operational planning and control. The ISMS now needs to establish criteria for actions identified in Clause 6 and control those actions in accordance with the criteria.
Additional minor changes include:
Clause 5.3 Organizational Roles, Responsibilities, and Authorities: A minor update to the language clarified that communication of roles relevant to information security are to be communicated within the organization.
Clause 7.4 Communication: Subclauses a-c remain the same. But subclauses d (who should communicate) and e (the process by which communication should be affected) have been simplified and combined into a newly renamed subclause d (how to communicate).
Clause 9.2 Internal Audit: This clause was changed, but not materially. It essentially just combined what already existed between Clause 9.2.1 and 9.2.2 into one section.
Clause 9.3 Management Review: A new item was added to clarify that the organization’s management review shall include consideration of any changes to the needs and expectations of interested parties. It’s important to note any changes, as they are instrumental to the scope of the ISMS that’s determined in Clause 4 (and based on those needs and expectations). For example, if an organization’s Board of Directors wants to go public, organizations must consider how the change in priorities would impact the ISMS.
Clause 10 Improvement: Structural changes to this clause now list Continual Improvement (10.1) first, and Nonconformity and Corrective Action (10.2) second.
Changes to Annex A control structure
In ISO 27001:2022 structural changes were made to the Annex A controls. Control groups have been reorganized and the overall number of controls has decreased.
At a high level:
11 new controls were introduced
57 controls were merged
23 controls were renamed
3 controls were removed
In ISO 27001:2013, controls were organized into 14 different domains. In the new update, controls are placed into the following four themes instead:
Organizational controls (37 controls)
People controls (8 controls)
Physical controls (14 controls)
Technological controls (34 controls)
The nomenclature change promotes a better understanding of how Annex A controls help secure information. The previous domain names were written for IT professionals — rather than management. Companies will need to update their Statement of Applicability to match this new structure, as they look to achieve certification under ISO 27001:2022.
Additional attribute values were also added to better describe the Annex A controls and help categorize them, but these are only available in ISO 27002.
New controls within ISO 27001:2022 Annex A
The largest change within Annex A is around the 11 new controls which were introduced. Organizations that are currently certified under ISO 27001:2013 will need to ensure proper processes are in place to meet these new requirements or will need to create new processes to incorporate these controls into their existing ISMS.
Notably “threat intelligence” requires organizations to gather and analyze information about threats, so organizations can take action to mitigate risk. Companies certified under ISO 27001:2013 may not have this element in place. This is a relevant change and speaks to the idea that threats are ever evolving. Therefore, mitigating risk is a continuous process, not a “one-and-done” task. This tracks back to an update in ISO 27002 which was introduced earlier in 2022. ISO 27002 can provide more clarity on this, as it includes additional implementation guidance.
Additional new controls within ISO 27001:2022 include:
A.5.7 Threat Intelligence: This control requires organizations to gather and analyze information about threats, so they can take action to mitigate risk.
A.5.23 Information Security for Use of Cloud Services: This control emphasizes the need for better information security in the cloud and requires organizations to set security standards for cloud services and have processes and procedures specifically for cloud services.
A.5.30 ICT Readiness for Business Continuity: This control requires organizations to ensure information and communication technology can be recovered/used when disruptions occur.
A.7.4 Physical Security Monitoring: This control requires organizations to monitor sensitive physical areas (data centers, production facilities, etc.) to ensure only authorized people can access them — so the organization is aware in the event of a breach.
A.8.9 Configuration Management: This control requires an organization to manage the configuration of its technology, to ensure it remains secure and to avoid unauthorized changes.
A.8.10 Information Deletion: This control requires the deletion of data when it’s no longer required, to avoid leaks of sensitive information and to comply with privacy requirements.
A.8.11 Data Masking: This control requires organizations to use data masking in accordance with the organization’s access control policy to protect sensitive information.
A.8.12 Data Leakage Prevention: This control requires organizations to implement measures to prevent data leakage and disclosure of sensitive information from systems, networks, and other devices.
A.8.16 Monitoring Activities: This control requires organizations to monitor systems for unusual activities and implement appropriate incident response procedures.
A.8.23 Web Filtering: This control requires organizations to manage which websites users access, to protect IT systems.
A.8.28 Secure Coding: This control requires secure coding principles to be established within an organization’s software development process, to reduce security vulnerabilities.
What should I do next?
The new ISO 27001:2022 standard must be fully implemented no later than October 31, 2025. For companies that are still operating under ISO 27001:2013, you will need to transition prior to the deadline to maintain certification.
Don’t panic. Creating a plan of action and moving quickly is essential to preventing a hack of valuable information. Enlist the help of a trusted audit partner to get you back on track. Our team of experts recommend that you:
- Conduct a gap assessment: An audit team can map your existing controls to the newly revised standard and determine what changes your company will need to make to achieve certification under the new version of the standard.
- Implement new controls: Once that assessment is complete, we recommend focusing on implementing new standards that align with ISO 27001:2022.
- Conduct a transition audit: To update your current certification, a transition audit is mandatory to move into the 2022 version. Get ready with our ISO 27001 checklist.
Choosing an auditor that prioritizes a high-quality report can assist with your transition to ISO 27001:2022. Menlo Security enlisted A-LIGN for its transition from ISO 27001:2013 to ISO 27001:2022 and appreciated the team’s attention to detail and responsiveness. “I have extensive experience with auditors, and working with A-LIGN has been refreshing,” said Rashpal Singh, Menlo Security Global Director of Governance, Risk, and Compliance. “I appreciate their approach, communication, proactive team, and how seamlessly audits are conducted with a no-surprises approach.”
Start the process of updating your ISMS to new standards. Contact us today.
As Artificial Intelligence (AI) continues to be adopted on a large scale, organizations are expected to show responsible usage and ensure their systems can be trusted with sensitive information. Our 2025 Compliance Benchmark Report, featuring insights from over 1000 compliance professionals worldwide, shows that 90% of organizations have an AI compliance policy in place or are working on one. This means that most organizations are thinking about the role AI plays within their operations and are working on documenting and training their teams on acceptable use and guidelines.
It’s a transformative tool for businesses, but CISOs and IT teams need to understand the risks and set requirements for responsible adoption. In this article, we’ll go through the risks of AI tools and provide practical tips to mitigate risks.
Key risks of AI tools
While AI offers significant opportunities, it introduces serious risks to data privacy and security. These are the major risks that your organization needs to be aware of:
AI learns from user input
By default, AI chatbots, like Chat GPT or Gemini, use a language learning model (LLM) to train themselves on information that is put into their system. When employees use personal accounts to access AI tools, they could inadvertently be training AI on sensitive client data or intellectual property.
AI reduces control over data
What happens to the data once it’s put into AI systems? Many AI tools, especially free versions, share information with third-party models without explicit consent, increasing the risk of data exposure and loss of control over the information.
AI threatens data privacy
If a user shares client data with an AI tool that doesn’t isolate data or ends up sharing it with a third-party model, the company is at major risk of violating privacy agreements, which can lead to its own set of legal problems.
AI complicates compliance efforts
Use of unregulated AI tools can cause inconsistencies in your organization’s compliance practices. Without policy and procedures to manage which tools are approved, it is easy for the problem to get out of hand quickly, leading to timely and costly overhaul down the road.
How companies can adopt AI responsibly
AI tools have risks, but there are effective strategies to manage them responsibly.
Establish an AI steering committee
Forming a steering committee is the key to guiding responsible AI adoption. A steering committee oversees both the internal and external use of AI tools, creating policies to mitigate the associated risks and educate its users.
The most effective steering committees are formed of stakeholders across the organization, and they work alongside AI initiatives rather than being gatekeepers of them. Including stakeholders from different departments helps drive the adoption of AI and ensures that all users understand how to mitigate the risks when using these tools. They support overall goals while ensuring new AI initiatives comply with regulatory standards. This keeps executives and investors happy and facilitates the strategic integration of AI across the organization.
Create an AI usage policy
It’s important to establish a policy to protect your company from liabilities that can come from using AI. This policy will serve as a guideline for how your company implements AI and ensures responsible usage. It’s also a crucial element for AI frameworks and regulations like ISO 42001 and the EU AI Act. Check out our AI Policy Template to learn the key elements and information to include.
Implement internal governance
Establishing governance around the tools used internally can help bolster AI security efforts. Here are steps you can take to proactively mitigate risks and get control over your company’s AI usage:
- First, get an inventory of all the AI systems that are being used throughout the company. Figure out what these tools are and what they do.
- Next, perform a basic AI impact assessment on each tool. This will help you determine the risks and benefits of each tool so you can decide if it’s worth keeping.
- From there, verify the security controls of each AI tool to determine if the service encrypts and isolates your company’s data from others. In many cases, you will need to purchase corporate licenses to enable security and privacy controls.
- Once you’ve gone through the first three steps, decide which tools will be sanctioned and which will be blocked. It’s highly recommended to establish a white-list only approach to new AI tools, meaning that by default all new AI tools are blocked unless they are requested by stakeholders, have a valid business justification, and undergo a required AI Impact Assessment.
- Finally, you should have an open conversation with the leadership team to get an understanding of which tools people use and value. Always be open to expanding the internal AI toolkit, as long as there is business justification as to why the sanctioned tools can’t be used.
Eventually, as your AI Usage Program matures, you can incorporate data loss prevention (DLP) to monitor the type of data that is being put into these systems. This involves classifying the data and defining what information is sensitive, confidential, and allowed to be inputted into the AI tools. This will allow you to safeguard your data and manage AI adoption at a high level.
Build your security around ISO 42001
ISO 42001 has become the leading standard for AI compliance, with major companies like Microsoft and Google racing towards certification. Even if your company isn’t planning on getting certified just yet, basing your security around ISO 42001 will facilitate faster certification if you start to receive pressure for it. Supply chains are already starting to favor those that have certification beyond just a simple trust document, so aligning with ISO 42001 can help give your organization a competitive advantage.
If you’d like to learn more about AI best practices and implementing ISO 42001, you can contact us here.
Compliance isn’t just a “nice to have,” but a “must have” to do business today. Which framework is top of mind for many organizations? ISO/IEC 27001:2022. This global leading certification is a common way to demonstrate trust, win new business, and drive results. Read on for a guide to your ISO 27001 audit.
What is ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 is an international standard for information security management systems. It provides a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information, ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability. The standard outlines requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continuously improving an organization’s ISMS.
Why should you conduct an ISO 27001 audit?
ISO 27001 isn’t a legal requirement but may be a prerequisite to customers doing business with your organization.
Some industries are more likely to need an ISO 27001 certification because of the type of data that companies store. These industries include:
- Information technology
- Healthcare
- Finance
- Consulting
- Telecommunications
Beyond a requirement of doing business, an ISO 27001 certification is a best practice for forward-thinking companies that care about cybersecurity. Successfully completing an ISO 27001 audit demonstrates to customers and other stakeholders that you care about protecting their data. Plus, it gives your organization a competitive advantage over similar vendors who might not have the same standards for data protection.
Preparing for your ISO 27001 audit
The prep work is just as important as the audit when it comes to compliance. Your organization should take the time to understand the standard, define your goals, and research certified third-party assessment organizations. You should also be willing to conduct a gap assessment and understand the state of your company’s compliance journey before jumping into an ISO 27001 audit.
How to select a certification body
Selecting a certification body is one of the most important parts of a successful ISO 27001 audit. This team will be responsible for evaluating and certifying your ISMS, so choosing a partner with experience and certifications is essential to a high-quality audit. Here are some things to consider before selecting a certification body:
- Accreditation: Your certification body must be certified by a recognized accreditation body to conduct an ISO 27001 audit and award your team a certification. For example, two top accreditation bodies include ANAB and UKAS. If your auditor does not have an accreditation, you will not have a valid certification after your ISO 27001 audit.
- Experience: Similarly, picking an experienced team is essential. You’ll be trusting this team to provide a high-quality ISO 27001 audit. Your chosen team should be trained and certified to provide a valuable audit experience.
- Technology-enabled audit process: Choosing an audit partner that uses technology to its fullest extent can help you get the most out of your audit. Technology keeps teams organized, projects on track, and sets your company up for success for future audits.
The ISO 27001 audit process: What to expect
There are several steps to your ISO 27001 audit. Your team should be prepared to identify gaps, work with your audit team, and implement changes based on any recommendations or findings to ensure a smooth process.
Pre-assessment
The ISO 27001 pre-assessment process is designed for companies that will undergo the certification process for the first time and is only performed on an as-needed basis. Organizations such as certification or implementation bodies, will simulate the actual certification audit by performing a review of your company’s entire management system including scope, policies, procedures, and processes to review any gaps that may exist and should be evaluated prior to conducting the ISO 27001 audit.
The pre-assessment phase can give your organization a head-start on the ISO 27001 audit process by revealing any oversights or potential weaknesses that your organization may have ahead of the certification audit so that you can act on areas that require remediation or attention.
Stage 1 audit
First, an auditor reviews an organization’s documentation to confirm it is following ISO 27001 requirements. The Stage 1 audit also checks to see if the required activities of the standard have either been completed or are scheduled for completion prior to starting Stage 2.
At the end of Stage 1, the auditor will determine if your company is ready to move forward to Stage 2 of the ISO 27001 audit process, or if there are any areas of concern regarding your company’s policies, procedures, and supporting documentation before proceeding. In rare cases where significant areas of concern are noted, you may be required to complete a second Stage 1 audit before moving on to Stage 2.
Stage 2 audit
The Stage 2 audit is performed to test the conformance of the system with the ISO 27001 standard. During this stage, the certification body will perform testing procedures including interviews, an inspection of documented evidence, and an observation of processes. Every audit is different in duration, and the time to completion is determined by several factors.
Upon completion of Stage 2, the certification body will determine if your organization is ready to be certified. If there are any major nonconformities, they will need to be remediated before a certificate can be issued. At this point, an organization is issued a certificate valid for three years, contingent on the continued successful completion of surveillance audits.
Surveillance audit
Obtaining ISO 27001 certification is not the end of the journey; it marks the beginning of a commitment to maintaining and improving information security practices. Surveillance audits are conducted annually after your initial ISO 27001 audit to ensure ongoing compliance with the standard’s requirements.
For the next two years, annual surveillance audits are required to ensure ongoing conformity with the ISO 27001 standard. These audits provide assurance that your systems and processes remain compliant over time. Surveillance audits are shorter in time and scope than the initial Stage 2 ISO 27001 audit and test a sampled set of controls. Typically, this process should take a few months to complete each year.
Recertification
Your ISO 27001 certificate is valid for three years after the issue date as long as the surveillance requirements are met. However, your organization will need to recertify before the expiration date, which will then restart the three-year certification process.
The recertification process differs from the initial certification, as organizations do not typically need to go through the Stage 1 audit again. Organizations begin recertification with a full system audit, which is similar to a Stage 2 audit. Upon completion of recertification, organizations will undergo further surveillance audits.
How long does an ISO 27001 audit take?
The duration of an ISO 27001 audit can vary depending on the size and complexity of your organization, the maturity of your information security management system, and your organization’s level of preparedness. Here’s a general overview of the time frame for each stage of the ISO 27001 audit process:
Pre-audit preparation
Before the actual audit begins, organizations typically spend several months preparing and implementing their ISMS. This phase includes conducting a gap analysis, developing and implementing security controls, and performing internal audits. The duration of this preparation phase can range from a few months to over a year, depending on the organization’s readiness and resources.
Stage 1 audit: Documentation review
The Stage 1 audit, also known as the documentation review, usually takes 1-2 days. During this phase, the auditor reviews the ISMS documentation to ensure it meets ISO 27001 requirements. The duration may vary based on the complexity of your ISMS and the thoroughness of your documentation.
Stage 2 audit: On-site assessment
The Stage 2 audit, or on-site assessment, will be dependent on the headcount supporting the ISMS, number of locations, and overall environment complexity. These factors will determine the number of days needed to perform the audit. During this phase, the auditor conducts interviews, examines records, and observes processes to verify that the ISMS is effectively implemented and maintained. The length of the on-site ISO 27001 audit depends on the size of your organization and the scope of the audit.
Post-audit activities
After the walkthrough portion of the audit, the auditor will provide a report detailing their findings. If there are non-conformities, your organization will need to address them within the defined timeline. The time required to resolve non-conformities and complete the follow-up audit can vary, but it generally takes a few weeks to a couple of months, depending on the severity.
The time it takes to complete an ISO 27001 audit will vary based on the size of your organization, how established your ISMS is, and the availability of your audit team.
Get started with your ISO 27001 audit
Navigating the ISO 27001 audit process can be challenging, but with proper preparation and commitment, your organization can achieve certification and reap the benefits of enhanced information security. By demonstrating your dedication to protecting sensitive data, you can build trust with customers, comply with legal requirements, and gain a competitive edge in the market. Contact us today to get started on your compliance journey.
More than 90% of organizations conduct at least two audits or assessments each year, and for larger organizations, that number continues to grow, according to A-LIGN’s 2025 Compliance Benchmark Report.
These days, compliance teams at large companies are spending their time tackling compliance challenges one by one, rather than developing a comprehensive strategy. This disjointed approach wastes time and money as duplicative audits and endless audit cycles strain compliance teams’ resources.
Enter audit harmonization: a premium service designed by A-LIGN’s industry experts to maximize efficiency and provide high-quality audits to enterprise organizations with three or more frameworks to consolidate. Throughout the process, A-LIGN will identify and consolidate overlapping requirements from audits across various vendors to reduce the complexity and burden on your internal resources.
Read on to learn how this strategy can alleviate the burden of your audit cycle.
What is audit harmonization?
Audit harmonization is a white-glove service for enterprises juggling multiple frameworks. Audit harmonization, at its core, is a service in which subject matter experts evaluate your current audit cycles and assessments and develop a plan that will streamline the process.
A-LIGN’s unique approach involves a three-step process to create a custom plan for your company that understands your goals, identifies overlapping requirements, and streamlines your efforts for an effective, high-quality audit. Our approach allows you to scale up to a robust suite of services. Enterprise customers can expect a dedicated team of highly experienced auditors who will support you throughout your compliance journey.
Why audit harmonization?
A-LIGN’s 2025 Benchmark Report found that the #1 challenge of the audit process for enterprise organizations is complexity in conducting multiple audits. These organizations are frequently conducting six or more audits per year to address their diverse compliance requirements and risk profiles. That puts some teams in a never-ending audit cycle. Audit harmonization consolidates the requirements where synergies can be achieved in both fieldwork and evidence collection, and keeps your team focused on the business, not the audits.
Beyond the time spent in audit cycles, enterprise organizations are also investing significant money on compliance. Large organizations in particular are making increased investments. The 2025 A-LIGN Compliance Benchmark Report found that 71% of enterprise companies spend over $100,000 on audits each year, whereas only 19% of small companies and 42% of medium companies say the same. Audit harmonization helps these businesses use a strategic approach for their cycles, reducing the number of duplicate tasks and saving money in the process.
Who is audit harmonization for?
A-LIGN designed the audit harmonization program with enterprise companies in mind. This service is best suited for large companies with three or more frameworks to adhere to.
Who will execute my audit harmonization process?
Your audit harmonization process will be led by a dedicated team who will offer tailored guidance to help you feel prepared and confident. This team will create a strong partnership focused on ongoing success and features A-LIGN’s expert team of auditors, including our leadership, to ensure you continuously receive the highest quality, white-glove service.
How does it work?
There are three steps to A-LIGN’s unique audit harmonization service: analyze, customize, harmonize. This process, handled by a dedicated team, ensures that your business and compliance goals remain top of mind throughout the audit cycle.
Here’s how it works:
Analyze: First is the discovery phase, where our team aims to understand the way your business operates, your organization’s objectives and the role of compliance in those objectives. A-LIGN identifies areas that may impact the audit scope, such as changes to the business, locations, headcount, processes, IT, software, and infrastructure.
Our information-gathering session results in a report that outlines the roadmap for your company’s audit. We’ll also determine the best time of year to conduct audits, recommendations, and provide a summary proposal.
Customize: After analyzing your existing program, our team presents recommendations and potential savings that can be realized in a master audit plan. This visual plan will:
- Identify audits with overlapping requirements to achieve synergies in fieldwork and evidence collection
- Recommend methods for strengthening your controls environment
Our subject matter experts will work closely with your team to deliver a strategy that is best fit for your team. After sharing our own recommendations, we’ll collaborate and adjust the plan as needed to ensure a customized path forward.
Harmonize: In accordance with your master audit plan, A-LIGN auditors review evidence, test it against the necessary compliance frameworks, and deliver a comprehensive final report upon conclusion of testing. Throughout the process, our team minimizes the amount of effort required and ensures you receive the highest quality audit.
During the process, you can expect to hear from your dedicated team regularly to ensure all plans are being upheld. The A-LIGN team will issue a final report and any follow-up items after completing field work. In addition, we will schedule annual business reviews to benchmark current projects against business objectives, to ensure you are successful in your compliance journey.
How to get started with audit harmonization
Interested in understanding how your company can benefit from audit harmonization? Contact us today to learn more.