SOC 2 Buyer’s Guide
SOC 2 is the most popular cybersecurity audit, and for good reason. This framework is the foundation for many organizations’ compliance strategies and is now an expectation to do business with customers in many industries.
Read on to learn why SOC 2 is so popular and how your organization can begin its compliance journey with a SOC 2 attestation. Follow along and download the guide here. In this guide, we will:
- Define SOC 2 and its criteria
- Explain the examination process
- Share best practices for choosing a quality audit partner
- Spotlight real-world SOC 2 success stories
- Give you a list of questions to evaluate potential audit partners
Defining SOC 2
What is SOC 2?
A SOC 2 report (System and Organization Controls) report is an independent attestation that evaluates the effectiveness of a company’s controls as they relate to Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy. The security of your environment is assessed against the requirements within a SOC 2 examination, known as the Trust Services Criteria (TSC):
- Security (required)
- Availability (optional)
- Processing Integrity (optional)
- Confidentiality (optional)
- Privacy (optional)
Who needs SOC 2?
Service organizations that process, store, or transmit data for their clients or partners need a SOC 2 attestation. While SOC 2 applies to almost any organization, it’s particularly important to data centers, software-as-a-service companies, and managed service providers.
Who can perform a SOC 2 audit?
Only licensed CPA firms that are accredited by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants can complete a SOC 2 audit.
What are the SOC 2 Trust Services Criteria?
SOC 2 is comprised of five TSCs. To determine which TSCs are best for your organization, it’s important to understand what type of data you store, process, and/or transmit.
- Security: Comprised of 9 control families ranging from organization and management to risk assessment, to logical security and change management. This criterion is required in every SOC 2 report.
- Availability: Addresses controls related to availability and redundancy of services to meet client SLAs. The Availability Criteria is a great add-on for most organizations.
- Processing Integrity: Addresses controls related to accurate processing of customer data without corruption or unauthorized alteration. Processing Integrity is largely specific to an organization’s services and not often applicable to all organizations.
- Confidentiality: Addresses controls related to protection of data deemed confidential between an organization and its client. This extends to any data deemed confidential. The Confidentiality Criteria is a great add-on for most organizations.
- Privacy: Addresses controls related to the protection of Personally Identifiable Information (PII). This is anything that can be tied to an individual. Privacy is large and cumbersome, and only applicable to organizations that store, process, or transmit PII.
The examination process
The SOC 2 examination process is a well-defined, six-step audit cycle. The steps include:
- Readiness assessment (optional)
- Audit planning
- Audit testing and review of evidence
- Closing meeting and draft report preparation
- Issuance of the final report
Understanding the steps is an essential part of preparing for your SOC 2 examination.
Building a partner team
Before beginning your audit, you may enlist the help of tools or partners that can help you maximize efficiency, accelerate outcomes, and drive continuous growth for your SOC 2 attestation. Government, risk and compliance software solutions frequently work in tandem with your auditor, especially if they are tech-enabled with an audit management platform. This partnership typically shows up in four steps:
- Laying the foundation: GRC tools can help you prepare for your SOC 2 audit by automating evidence collection in addition to managing policies and procedures related to your audit.
- Accelerating with intelligence: This is where your audit partner begins their work. Choosing a tech-enabled auditor means that they can generate request lists, match evidence, and deduplicate requests across frameworks if you are conducting multiple audits, all powered by AI.
- Realizing results: This stage will include your audit partner conducting assessments, reviewing evidence, and delivering your final report.
- Proving compliance at scale: After you’ve earned your attestation, it’s time to show it off to the world. GRC tools can help you showcase and provide automated, secure access to accreditations to potential buyers, saving your team time and effort on manual approvals and questionnaires.
In addition to these steps, GRC tools provide continuous monitoring, which keeps your team in the loop on potential issues and areas for improvement long after you’ve completed your first attestation.
The readiness assessment
Readiness assessments are an optional way for your organization to understand the current state of your compliance before entering an audit cycle. These assessments can give your team the confidence to prepare for your SOC 2 examination. Your audit partner may take one of two approaches with these assessments:
- Traditional approach: Your auditor will perform a formal Readiness Assessment that simulates a Type 1 or Type 2 audit and results in a report with recommendations from the auditor. This option is recommended for companies that don’t have many formal procedures or have never been through an audit before.
- Belay approach: This hybrid two-step approach has a smaller high-level gap assessment of key controls prior to the Type 1 SOC 2 examination. This approach saves time and costs and is designed for more mature organizations with formally established and implemented procedures who still have concerns or questions about their readiness for a SOC 2 audit.
Scoping
During the scoping phase, your auditor team will work with your organization to better understand the scope of services as well as to identify and evaluate the controls in place specific to the scope of services. The auditors will also work with your organization to further explain the SOC 2 framework and TSCs.
Audit planning
Once your organization has secured plans to engage a SOC 2 with an auditor, you will be introduced to the audit management team to begin the planning phase of your audit. An official kickoff call will be scheduled to discuss timing of the audit and share key planning information and provide an Information Request List (IRL) relevant to the defined scope. Your organization should review each of the requests within the IRL to ensure you understand what is being requested, then begin to gather and provide the requested evidence to the auditors. As the dedicated audit testing date nears, the audit team will set up regular touchpoints with you to answer questions and encourage your organization to upload as much evidence as possible to and audit management platform like A-SCEND or your GRC tool of choice prior to the start of testing.
Testing and reviewing of evidence
At this stage, the assigned auditor actively reviews all evidence and completes the required testing, which is either performed remotely, onsite or a combination of both (depending on scope). It is essential that a majority of evidence is uploaded before this phase begins. During the testing and review of evidence phase, the auditor performs the following tasks:
- Explains testing approach based on the SOC 2 requirements
- Confirms the key processes and procedures observed relevant to the scope of services and provides feedback on the system description
- Holds meetings with process owners to understand the controls in place and operation
- Reviews evidence to corroborate management’s controls and completes testing of those controls utilizing the evidence that has been provided in the planning phase
- Asks clarifying questions relating to the evidence provided and processes observed
- Requests additional evidence needed in support of testing the scope of services
- Identifies and proactively communicates potential findings identified in the testing
- Proactively communicates the status of testing and roadblocks encountered
Closing meeting and draft report
Step four begins once all evidence has been provided, reviewed and accepted by the auditor. Your auditor then performs various rounds of quality review, involving multiple levels audit management, and prepares a draft version of the report. When the draft report is delivered, it is accompanied by a management representation letter that must be signed by an appropriate member of the organization and returned to your audit team. Management will have an opportunity to review the draft report prior to final issuance.
The final report
Once you have reviewed and returned the signed management letter and draft report with your comments and suggested updates, the auditor works to finalize the report, which includes addressing any comments left by your organization. Once all comments are addressed and updates applied, the report is finalized and delivered to your organization electronically (a hard copy can also be requested). For more about these steps, download our SOC 2 Buyer’s Guide.
Selecting a quality audit partner
Choosing the right auditor can make all the difference during your examination process. Quality auditors will drive efficiencies for your team and instill confidence in customers that your SOC 2 attestation is reputable and meets a high standard.
There are many ways to define what makes up a quality audit partner. Here are a few considerations to keep in mind when evaluating potential auditors.
Experience and credentials
A potential partner’s experience and credentials is one of the first things you should evaluate when choosing an auditor. Look for partners that have been in business for a long time and have a track record of success. In addition to reputation, technical credentials are important. Is this auditor accredited with the AICPA? Only independently licensed CPAs can issue SOC 2 attestation reports.
Report quality
Not all reports are created equal. High-quality audit reports won’t just confirm your compliance; they will highlight areas for improvement and risk mitigation strategies that are specific to your organization’s security posture. The AICPA has developed a downloadable checklist to guide management during their review of a SOC 2 to evaluate the sufficiency and quality of the report.
Tech-enabled services
Choosing an auditor that embraces technology isn’t a preference anymore, it’s essential. Auditors that perform all audit tasks manually will take longer to finish your audit and may be less accurate. We recommend partnering with an auditor that uses their own audit management platform to streamline the process. Additionally, you should enlist the help of an audit partner that integrates with your existing compliance and trust management software.
Audit process
It’s essential to understand the process that your chosen audit partner will use to complete your SOC 2 examination. Be sure to ask any potential partners about the timeline, scoping, audit cycle synchronization, and team communication before moving forward.
Case study: Obsidian Security
Obsidian Security is a market leader in comprehensive SaaS security, specializing in threat management integration, third-party risk, security posture and configuration, and compliance.
Obsidian’s path toward creating a robust security program started when the team only had 15 employees and a tight budget. Although they were a small team, Obsidian secured business from multinational, highly regulated customers with complex security needs.
The company reached a point of inflection where they needed to scale their compliance program and meet the growing demands of their enterprise customers. With their sights set on obtaining a SOC 2 report, Obsidian looked for an audit partner to help them meet their compliance goals.
Obsidian sought a high-quality report and efficient audit process, driven by a partnership focused on continual improvement. Ultimately, Obsidian chose to engage with A-LIGN and Drata for their audit and GRC requirements.
Obsidian has implemented a robust third-party risk management program, which involves thorough scrutiny of attestation reports from various companies, so their team has ample knowledge on what makes a trusted high-quality, robust audit report.
Of all the assessors’ reports, Alfredo said A-LIGN’s stands out for its well-structured and comprehensive nature, particularly in assessing performance and coverage of controls. The detailed report assures customers and prospects of proper due diligence and fosters trust with other key stakeholders.
“The value proposition of having an audit partner like A-LIGN at the strategic level and having a partner like Drata at the technical and operational level is that you can streamline the entire audit process.”
– Alfredo Hickman, CISO, Obsidian Security
Checklist: Questions to ask your audit partner
Choosing an audit partner is one of the most important steps to completing a SOC 2 attestation for your organization. This decision will impact every other step – from start to finish, your assessor will be with you through it all. This SOC 2 checklist details questions that we recommend you ask any potential assessor.
- What is your experience with SOC 2 attestations?
- Is your company accredited by the AICPA?
- How many SOC 2 attestations have you completed?
- How many SOC auditors does your team have?
- Do you have experience conducting SOC 2 attestations in my industry?
- Does your organization conduct other audits?
- Are we able to pursue multiple frameworks at the same time with your organization? How does your team handle this?
- Do you have experience identifying overlaps among multiple frameworks?
- What can I expect during the audit process?
- Does your organization use technology to enhance the audit process?
- What is your response time to questions from our team?
- How do you ensure the quality of your audits?
- How do you define quality?
- What sets your audit process apart from other audit firms?
- How much will my SOC 2 attestation cost?
- What are your rates and what do they include?
- How long does a SOC 2 attestation take with your organization?
- How long will each step of the process take?
- Do you have references and case studies from satisfied customers?
Next steps
If you’re ready to take the next step, contact A-LIGN today to begin your journey to SOC 2 compliance. The A-LIGN difference is:
- 17.5k+ SOC assessments completed
- #1 SOC 2 issuer in the world
- 200+ SOC auditors globally
A-LIGN is the leading provider of high-quality, efficient cybersecurity compliance programs. Combining experienced auditors and audit management technology, A-LIGN provides the widest breadth and depth of services including SOC 2, ISO 27001, HITRUST, FedRAMP, and PCI. A-LIGN is the number one issuer of SOC 2 and a leading HITRUST and FedRAMP assessor.
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) is now a contractual requirement for organisations doing business with the US Department of Defense (DoD) starting 10 November 2025.
This marks the beginning of Phase 1 of the CMMC rollout, and from this date forward, any organisation — regardless of its headquarters location — must demonstrate CMMC compliance to be eligible for new US DoD contracts.
Why this matters for UK and European companies
Organisations that handle Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) or Federal Contract Information (FCI) as part of their work with the DoD or its prime contractors are required to be CMMC certified by a certified third-party assessor organisation (C3PAO).
According to The Cyber AB, the official accreditation body for CMMC, there is no reciprocity with other cybersecurity standards — including ISO 27001, NIS2 Directive, or GDPR. All contractors, whether US-based or international, must follow the same certification process, with no exceptions.
What you should do now
Start early! The average preparation time for a CMMC Level 2 assessment is 9 to12 months. With limited C3PAO availability and rising demand, early engagement helps you avoid delays and stay ahead of competitors. Here are some steps to get started:
STEP 1. Identify your CMMC level:
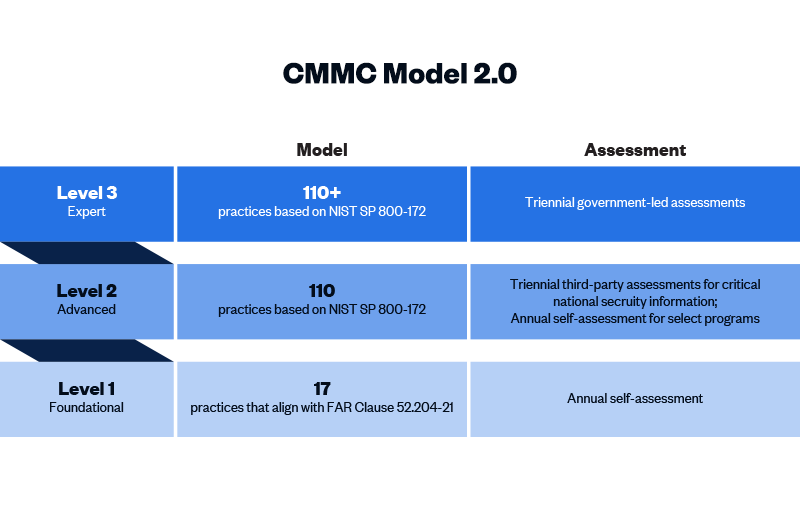
Level 1 [Foundational]: Applicable to defence or aerospace contractors bidding on DoD contracts handling FCI. All contractors in Level 1 must implement 17 basic cybersecurity practices to safeguard FCI. If the FAR 52.204-21 requirement is in your current contracts, you are most likely in the CMMC Level 1 category.
Level 2 [Advanced]: Applicable to defence or aerospace contractors bidding on DoD contracts handling:
- CUI
- CTI
- ITAR or export-controlled data that is CUI
- All contractors in Level 2 must implement 110 security controls from NIST 800-171. If the DFARS 252.204-7012 requirement is in your current contracts, you are most likely in the Level 2 category.
Level 3 [Expert]: Applicable to defence or aerospace contractors bidding on DoD contracts handling Critical CUI. Level 3 security requirements are expected to contain a subset of NIST SP 800-172. If the DFARS 252.204-7012 requirement is in your current contracts and you have had a DIBCAC assessment, you are most likely in the Level 3 category.
STEP 2. Identify in-scope assets such as Federal Contract Information (FCI) and Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI).
STEP 3. Identify gaps by performing a gap assessment.
STEP 4. Develop an implementation plan based on findings from your gap assessment and address vulnerabilities to meet the control objective requirements.
STEP 5. Engage a C3PAO: Because CMMC is a rigorous cybersecurity framework, it’s critical to engage with a C3PAO that has extensive US federal expertise with frameworks such as FedRAMP. There are a limited number of C3PAOs authorised to conduct CMMC assessments, and not all are created equal. We recommend seeking out a C3PAO that has deep experience in US federal compliance, delivers high-quality final reports, and streamlines the process. To learn more about choosing the right C3PAO, download our CMMC Checklist.
How A-LIGN can help
A-LIGN is the only leading American C3PAO with offices in Europe. For companies headquartered in the UK and Europe, this means having access to deep US federal expertise with the convenience of local support in your own time zone.
We’ve completed over 1,000 US federal assessments, including:
- CMMC: Certified C3PAO with extensive readiness experience.
- NIST 800-171: The foundation of CMMC Level 2.
- FedRAMP: Top 3PAO with 100% authorisation success rate. A-LIGN’s A-SCEND is one of a few audit management platforms to be FedRAMP 20x authorised.
- GovRAMP: The only registered assessor currently on the market.
A-LIGN offers fast onboarding, with CMMC kick-off in just 6–8 weeks—twice as fast as the industry average—and streamlined support, with tailored guidance for international companies and a local presence in Europe.
Ready to start your CMMC journey? Book a meeting with A-LIGN today and get expert support on your timeline, in your region.
CISO insights: Empowering compliance teams through continuous compliance and smarter risk management
The role of the Chief Information Security Officer has never been more complex — or more critical. With cyber threats evolving daily, regulatory expectations tightening, and transformative technologies like AI entering the enterprise at full speed, today’s CISOs face the challenge of balancing operational efficiency, security maturity, and compliance at scale.
In this blog, longtime security expert and RegScale CISO Dale Hoak will share:
- Key trends CISOs should be watching, like Continuous Controls Monitoring, managing the risks of AI, third-party risk management, and collaborating across their organization.
- Practical strategies for managing risk including frameworks centered around AI, tools for continuous compliance and oversight, and tightening controls.
- How to turn security into a competitive advantage that can help your organization stand out in a crowded marketplace, drive efficiency, and build customer trust.
Read on to learn how to implement these tactics in your organization’s overall compliance strategy.
Key trends CISOs should be watching
1. Continuous compliance is replacing point-in-time audits
Annual audits and periodic assessments are increasingly insufficient for modern risk environments. The shift toward Continuous Controls Monitoring (CCM) enables organizations to collect and validate evidence in near real-time, reducing the window of exposure when controls drift or fail. This evolution ensures security and compliance posture are “always on” rather than a snapshot in time.
2. AI as a double-edged sword
AI is rapidly becoming a core tool for security operations, compliance automation, and risk detection. However, the same technology is being weaponized by threat actors to create more convincing phishing campaigns, automate reconnaissance, and exploit vulnerabilities faster. CISOs must view AI as both an enabler and a risk vector, building governance frameworks to control its use internally and defend against it externally.
3. Prioritizing supply chain and third-party risk management
Recent high-profile breaches have underscored the reality that your security is only as strong as the least secure vendor in your supply chain. Increasing regulatory focus, including requirements for real-time vendor monitoring, makes proactive third-party risk management a top priority.
4. Convergence of security and compliance functions
Historically separated teams are increasingly being integrated under the CISO’s leadership. This convergence drives efficiency but also demands tools that support both compliance reporting and operational security in a single pane of glass.
Get ahead: Strategies to mitigate security risks and embrace AI safely
It’s not enough to just keep up in the world of compliance; CISOs and their teams need to look ahead when it comes to protecting sensitive data, obtaining new certifications, and handling third-party risk management. I recommend CISOs consider the following strategies to keep their organizations ahead of the next cyberattack.
1. Build a risk-based AI adoption framework
Before deploying AI, classify its use cases, assess related risks, and apply guardrails. Include policies for data privacy, ethical use, and model transparency. Partner with compliance experts to ensure AI deployments meet applicable regulations and industry standards.
2. Leverage CCM
Your systems are only as secure and compliant as the controls that govern them. Continuous Controls Monitoring ensures that controls, particularly those that are AI-related (e.g. access restrictions, data handling policies, and model retraining procedures) remain in effect over time.
3. Tighten identity and access controls
A single compromised account in your system can cause exponential damage. Integrate identity governance, conditional access, and multi-factor authentication into your compliance program to reduce the attack surface.
4. Expand third-party oversight
Ensure all your vendors meet your organization’s security and compliance standards. Continuous vendor monitoring should be non-negotiable.
Beyond compliance: Turning security into a competitive advantage
The most mature organizations recognize that compliance isn’t the ceiling; it’s the floor. In other words, meeting compliance is a bare minimum requirement that should automatically result from robust security and risk management processes.
But compliance isn’t just a basic necessity; it’s also a competitive advantage. By embedding security and compliance into daily operations, CISOs can deliver measurable ROI in several ways:
- Customer trust: Transparent compliance reporting builds confidence with clients, partners, and regulators.
- Operational efficiency: Automated evidence collection and reporting cut manual workloads by up to 70%, according to RegScale’s 2025 State of CCM Report.
- Faster market entry: Streamlined compliance processes enable quicker product launches in regulated markets.
The path forward
Cybersecurity leadership is at a crossroads. Emerging threats, evolving compliance mandates, and the promise (and peril) of AI are reshaping what it means to be a CISO.
By embracing Continuous Controls Monitoring, aligning AI use with risk governance, and integrating security and compliance into a unified strategy, CISOs can transform regulatory obligations into operational strengths.
The next era of cybersecurity won’t wait. The time to act — and automate — is now.
About Dale Hoak
Dale Hoak is a results-driven cybersecurity leader who has delivered measurable impact across the U.S. Navy, law enforcement, and corporate sectors. As CISO at RegScale, he secured critical certifications—including SOC 2, FedRAMP High, and CSA STAR—enabling expansion into regulated markets. His AI-driven security automation enhanced compliance capabilities and unlocked over $1M in additional revenue. At the NYPD, he established the first fully operational Security Operations Center (SOC), slashing incident response times. Previously, he led global cybersecurity transformations, securing 45K+ endpoints and managing 37 major security events. Dale excels at aligning security with business growth, ensuring resilience in high-stakes environments.
About RegScale
RegScale is a Continuous Controls Monitoring (CCM) platform designed to be the operational risk tool for the CISO. Built on a compliance as code foundation, RegScale enables extreme automation with our API-first strategy, self-updating paperwork, and powerful AI agents that all but eliminate manual labor and make your program more proactive — helping you save money, accelerate time to market, and reduce risk in your operational environment. Heavily regulated organizations, including Fortune 500 enterprises and the federal government, use RegScale and report achieving compliance certifications 90% faster and trimming audit preparation efforts by 60%, thereby strengthening security and reducing costs. Learn more at www.regscale.com.
The U.S. government’s use of cloud technology brings new opportunities and risks. To protect sensitive federal data, robust security measures are not just recommended — they are required. Any organization planning to do business with a federal agency must understand these requirements.
One of the most important federal standards is the Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program, or FedRAMP. This page provides a comprehensive overview of the FedRAMP authorization process, its benefits, and recent updates every organization should know.
What is FedRAMP and why is it important?
FedRAMP, launched in 2011, is a government-wide program designed to standardize cloud security assessment, authorization, and continuous monitoring for cloud products and services used by federal agencies. Its primary goal is to accelerate secure cloud adoption across government bodies by implementing a unified and rigorous set of security controls.
By establishing a consistent baseline for evaluating and authorizing cloud services within the federal government, FedRAMP helps agencies trust the security of cloud offerings through ongoing monitoring and proven best practices. Achieving FedRAMP authorization demonstrates a cloud provider’s commitment to comprehensive federal security standards and is a critical step for providers aiming to do business with federal agencies.
Who needs FedRAMP authorization?
If you are a Cloud Service Provider (CSP) selling cloud offerings to U.S. federal agencies, you must obtain FedRAMP authorization. Federal policy mandates that only cloud systems with FedRAMP authorization can be used by agencies for data storage or processing.
Does FedRAMP apply globally?
Yes. International companies providing cloud solutions to U.S. federal customers must meet FedRAMP requirements.
Key benefits of FedRAMP authorization
Federal organizations are required to only use CSOs that are FedRAMP authorized when purchasing cloud services. Because of this mandatory compliance requirement, the main benefit of FedRAMP is enabling your organization to do business with federal agencies. However, there are other benefits to FedRAMP:
- Allows a single Authority to Operate (ATO) to be used across all federal agencies
- There is only one assessment, saving time and money
- Streamlines the assessment process, saving time and money
- Designed specifically to meet the needs of CSPs
How to get FedRAMP authorized
Achieving FedRAMP authorization is accomplished through Agency Sponsorship, where a federal agency works directly with a CSP to sponsor their FedRAMP authorization process. CSPs collaborate with the sponsoring agency throughout the authorization process to achieve an ATO.
The Agency Authorization process involves:
- An optional, yet highly recommended, FedRAMP Ready assessment
- Pre-authorization activities, such as preparing the System Security Plan (SSP)
- Achieving agency authorization, where the agency issues an ATO
- Continuous monitoring post-authorization to maintain compliance
What is FedRAMP 20x?
FedRAMP 20x is an initiative designed to accelerate the path to FedRAMP Low and Moderate authorization through simplifying processes and leveraging automation. A significant benefit of this program is that it allows a CSP to pursue authorization without needing an agency sponsor, addressing long-standing challenges around approval times and processes. This program, announced in March 2025, introduces key improvements, including:
- Automation of compliance: Using machine-readable processes to reduce manual tasks
- Continuous monitoring: Validating security through real-time data instead of periodic audits
- Direct collaboration: Encouraging more agile relationships between CSPs and federal agencies
- Rapid innovation: Eliminating delays to enable faster adoption of secure cloud services
FedRAMP assessment and authorization process
The assessment process follows a standardized set of steps:
- Preparation phase: The provider completes a comprehensive SSP for the cloud service. Afterwards, a FedRAMP-approved 3PAO develops a Security Assessment Plan.
- Full security assessment: The assessment organization submits a Security Assessment Report (SAR), and the provider creates a Plan of Action & Milestones (POAM). The security assessment involves evaluating the company’s policies and procedures against NIST 800-53 controls to test and validate security authorizations. Once security authorization is granted, continuous assessment and authorization guidelines must be in place to uphold that authorization.
- Authorization: The authorizing agency determines whether the risk as described is acceptable. If confirmed, they submit an ATO letter to the FedRAMP project management office. The provider is then listed in the FedRAMP Marketplace.
- Continuous monitoring: The provider sends monthly security monitoring deliverables to each organization using the service.
What’s the timeline of a FedRAMP assessment?
Before beginning the formal assessment, it’s crucial to conduct a gap analysis to identify and address any vulnerabilities in your system. This preparation ensures your organization is ready to navigate the FedRAMP process efficiently and achieve compliance.
Step 1: Pre-assessment review (1-4 Weeks)
Step 2: Planning activities (4 Weeks)
Step 3: Assessment activities (7 weeks)
Step 4: Reporting activities (5 weeks)
Step 5: Sponsor issues ATO (2-3 weeks) and listed in the FedRAMP Marketplace
Step 6: Maintain authorization (Ongoing)
How long is FedRAMP valid?
A FedRAMP Ready designation is only valid on the Marketplace for twelve months.
What are the impact levels of FedRAMP compliance?
FedRAMP categorizes cloud systems into impact levels to ensure appropriate security measures are applied based on the sensitivity of the data and the potential risks of a breach. These levels guide organizations in implementing the necessary controls to protect federal information.
- Low impact SaaS (LI-SaaS): LI-SaaS is a subset of the low impact level and typically includes over 50 controls that require independent assessment. This baseline is designed for SaaS applications that do not store personally identifiable information (PII) beyond basic login credentials, such as usernames and passwords. Organizations achieving LI-SaaS authorization would experience minor adverse effects in the event of a loss of confidential information.
- Low impact level: This level includes approximately 156 controls. Organizations achieving low authorization status would experience limited adverse effects if a loss of confidential information occurred.
- Moderate impact level: Moderate impact includes around 323 controls and applies to the majority of organizations. A loss of confidential information at this level would have a serious impact on the organization.
- High impact level: High impact includes approximately 410 controls and is primarily for organizations working in law enforcement, emergency services, financial systems, and health systems. A loss of confidential information at this level could have catastrophic consequences.
FedRAMP vs. other federal frameworks
FedRAMP is a crucial standard for cloud services, but it’s part of a larger ecosystem of federal compliance frameworks. Understanding how it differs from other key standards can help you determine the right path for your organization.
FedRAMP vs. FISMA
The Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA) requires federal agencies to develop, document, and implement an agency-wide security program. The Risk Management Framework (RMF) is the process used to implement FISMA requirements.
While both FedRAMP and FISMA/RMF are based on NIST guidelines, they have a key difference in their authorization process.
- FedRAMP: Designed for CSPs, FedRAMP follows an “assess once, use many” model. A single FedRAMP authorization can be leveraged by any federal agency, making it a more efficient path for CSPs serving multiple government clients.
- FISMA/RMF: This authorization is specific to a single agency. If a provider needs an ATO for more than one agency, a separate FISMA/RMF assessment may be required for each one. This one-to-one design means authorizations are completed on an agency-by-agency basis.
FedRAMP vs. GovRAMP
Previously known as StateRAMP, GovRAMP was rebranded to reflect its expanded mission to support state, local, and educational (SLED) government entities.
- FedRAMP: Focuses exclusively on federal government agencies.
- GovRAMP: Provides a standardized security framework for cloud vendors working with state and local governments, as well as higher education institutions. It uses NIST 800-53 as its foundation, similar to FedRAMP, but is tailored to the needs of non-federal government bodies.
FedRAMP vs. CMMC
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) is a framework required for organizations within the Department of Defense (DoD) supply chain. Its primary focus is on protecting Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI).
- FedRAMP: Applies to cloud products and services sold to any federal agency.
- CMMC: Mandatory for all organizations doing business with the DoD. The requirements vary based on the sensitivity of the information the contractor handles.
How to prepare for FedRAMP authorization
Starting the FedRAMP journey requires careful planning and preparation. Following a structured approach can help you navigate the process efficiently and avoid common pitfalls.
- Research your target agency: Identify which federal agencies align with your services and understand their specific needs and priorities.
- Conduct a gap analysis: Before diving into the formal assessment, perform a readiness assessment. This helps identify any gaps between your current security posture and FedRAMP requirements, allowing you to remediate issues early.
- Develop a System Security Plan: The SSP is the security blueprint for your system. This comprehensive document details your security controls and how they meet NIST 800-53 requirements. It should be fully developed and reviewed before the formal assessment begins.
- Engage a 3PAO: A FedRAMP-accredited 3PAO will conduct your security assessment and provide an independent report on your compliance.
Why Choose A-LIGN for your FedRAMP journey?
Navigating the complexities of FedRAMP requires deep expertise and a proven track record. A-LIGN is one of the few globally recognized cybersecurity providers that offers a single-provider approach for a wide variety of security frameworks, including FedRAMP, FISMA, CMMC, and more.
As a top 3 FedRAMP assessor with over 1,000 completed federal assessments, our dedicated team provides tailored solutions that meet your specific compliance objectives. Contact us today to get started.
The final rule in CMMC 2.0 is finally here: 48 CFR. But what does it mean for you? If you’re doing business with the DoD (or plan to in the future), read on to learn how the official start of the Phase 1 CMMC rollout will impact your organization.
What is 48 CFR?
The CMMC 48 CFR is the final rule and that makes CMMC enforceable in DoD contracts. The rule was published in the Federal Register on September 10, 2025 with an effective date of November 10, 2025. This marks the official start of Phase 1 of the CMMC roll out, meaning readiness is no longer optional and all new DoD solicitations and contracts include some level of CMMC requirement.
What’s next?
CMMC requirements are now included in all new DoD solicitations and contracts going forward, and compliance is mandatory for award.
With implementation underway, the time to act is now. If you haven’t taken your place in the queue to begin your CMMC certification, contacting a C3PAO should be high on your priority list.
Learn about the standard
Understanding CMMC and the level of compliance that your organization will need to meet is key to a successful audit cycle. If you’re starting from scratch, our CMMC Buyer’s Guide will spell out the standard and levels of compliance, the assessment journey, and how to prepare based on your level of compliance.
Selecting a C3PAO
The Cyber AB authorizes a CMMC Third Party Assessment Organization (C3PAO) to contract and manage CMMC assessments. Only authorized C3PAOs can conduct CMMC assessments.
There are a limited number of C3PAOs authorized to conduct CMMC assessments, and not all are created equal. We recommend seeking out a C3PAO that has deep experience in federal compliance, delivers high-quality final reports, and streamlines the process. To learn more about choosing the right C3PAO, download our CMMC Checklist.
The A-LIGN difference
If you’re ready to take the next step toward CMMC compliance, contact us today. The A-LIGN difference is:
- Deep federal expertise with 1,000 federal assessments completed and more than 50 federal global staff.
- A quick start to CMMC with a kickoff in just 6-8 weeks alongside our experienced federal team. The industry average is 2x this timeline.
- Scalable support to be ready even while other C3PAOs get inundated.
Don’t get left behind. Reach out today to learn how A-LIGN can help you navigate this next step in your compliance journey.
The Case for Consolidating Your SOC 2 and ISO 27001 Audits
SOC 2 and ISO 27001 are practically household names in the world of compliance. These standards used to demonstrate proactive compliance across industries, but are now frequently a baseline expectation. Their popularity has surged in recent years due to customer requests and internal compliance posturing. The expectation to be compliant with these standards is expected to continue growing.
Beyond their popularity, did you know that SOC 2 and ISO 27001 have a lot in common? The control overlaps between these standards mean that if you’re pursuing one of these audits, it makes sense to do the other at the same time to achieve efficiencies during the audit cycle and reduce duplicative efforts. Read on to learn about the overlaps between SOC 2 and ISO 27001 and how harmonizing your audit cycles to pursue both frameworks at once can help your organization work smarter, not harder.
Understanding SOC 2 and ISO 27001
Before we dive into the similarities between these two standards, let’s break down the basics of each standard and what they are designed to do.
What is SOC 2?
A SOC 2 report (System and Organization Controls) is an independent attestation that evaluates the effectiveness of a company’s controls as they relate to Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, and Privacy. The security of your environment is based on the requirements within a SOC 2 examination, known as the Trust Services Criteria (TSC):
- Security (required)
- Availability (optional)
- Processing Integrity (optional)
- Confidentiality (optional)
- Privacy (optional)
What is ISO 27001?
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) originally published ISO 27001 in October 2005, revised in 2013, and again in 2022. It focuses on building a strong information security management system (ISMS) within organizations.
As one of the most widely used security frameworks around the world, ISO 27001 is a risk-driven standard that focuses on data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. The standard aims to help organizations have a stronger, more holistic approach to data security.
Overlaps between SOC 2 and ISO 27001
Despite their differences, SOC 2 and ISO 27001 have a sizable overlap at 43%, meaning that if you’ve already completed a SOC 2 assessment, you’ve already met 43% of evidence required for ISO 27001.
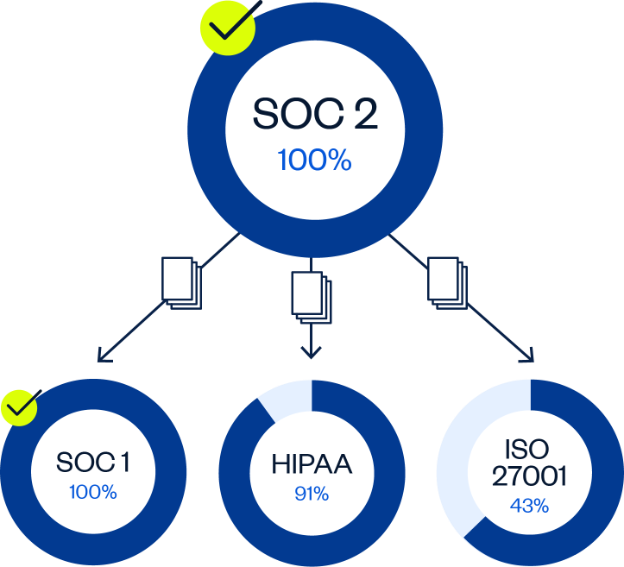
The key similarities in the controls between these two standards include:
- Positive security culture
- Risk identification, assessment, and mitigation
- Internal communication and collaboration
- Access control, authentication, and authorization
- Monitoring and logging of security events
- Timely identification and communication of control issues
Why should you consolidate your SOC 2 and ISO 27001 audits?
The process of consolidating your audits by identifying commonalities between frameworks and reducing duplicative tasks while completing both audits is often called audit consolidation.
This process is designed for organizations completing two or more audits per year to save time, save money, and power efficiencies across compliance teams.
Benefits of audit consolidation
Audit consolidation is a process designed to help you and your team get back to work and stop performing duplicative tasks every audit cycle and operate under continuous audit cycles. Although it may seem like a minor inconvenience to upload identical documentation to multiple places, that time adds up, and it’s precious. Audit consolidation can change all of this and help you:
- Save time by reducing duplicative tasks and documentation
- Drive efficiencies across your team by letting you get back to your real job
- Simplify the audit cycle and how it impacts your organization
Audit harmonization
If you have more than three audits to complete per year, your organization may benefit from audit harmonization, which is a white-glove approach to consolidating multiple frameworks.
There are three key steps to audit consolidation: analyze, customize, harmonize.
- Analyze: Our experienced audit team will take the time to understand your organization’s objectives, which frameworks you’re pursuing, and define how this compliance strategy can help you meet your goals.
- Customize: This step is centered around customizing the strategy presented to your team to consolidate your audit cycle. This step includes a Master Audit Plan and will present the time savings possible through audit consolidation.
- Harmonize: The A-LIGN team will execute the Master Audit Plan presented and minimize the amount of effort required for your compliance team. They will also ensure you are getting the highest quality audit on the market.
Audit consolidation FAQ
This process might be brand new to you, and that’s ok! Here are answers to some common questions about making the most of your audit consolidation process between SOC 2 and ISO 27001:
Can I consolidate audits with multiple providers?
One way to drive audit consolidation is through consolidating your audits with a single provider. This step can greatly simplify your audit cycles and reduce the complications of communicating with multiple teams, sharing status updates between providers, and staying organized during your audit cycle.
Who is involved in the audit consolidation process?
This isn’t just your immediate internal team, it’s your audit partner, your GRC tool, and any other people or programs that help you cross the finish line. We will take the time to understand your business in order to provide the most effective process. Have a GRC tool already in place? We partner with many major GRC platforms to increase efficiency in the process
Are there any other tools that can help my team consolidate our audits?
Technology is a huge piece of the puzzle that makes up audit consolidation. Tools that can offer access to historical data, leverage evidence across audits, and help your auditor work smarter are going to mean your audit cycle is greatly simplified.
Choosing the right audit partner
Choosing the right audit partner to consolidate your SOC 2 and ISO 27001 audits is key to a successful, high-quality final report. If you choose the right audit partner, you’ll be working in lockstep with this team year after year. Evaluate your options carefully before signing a contract. We recommend choosing a partner that:
- Is experienced across frameworks: Choosing a partner that can complete all of your audits in one place is essential to the consolidation process. After all, you can’t consolidate with one partner if they can’t execute an ISO 27001 audit and you need that certification to do business with a customer. Or, if ISO 42001 is on your compliance roadmap, ensure your audit partner can grow alongside you and provide new certifications.
- Has high standards of quality: Although quality is subjective, you should be looking for a final report that is detailed, provides actionable recommendations, and an audit team that prioritizes customer communication and education. These attributes demonstrate than an audit partner will be able to provide your organization with a high-quality final report that both confirms compliance and highlights areas for improvement and risk mitigation strategies that are specific to your organization’s security posture. Read more in our Quality Audit Checklist.
- Is tech-enabled: Choosing an auditor that is tech-enabled is all about efficiency. An auditor who does everything manually will take longer to finish your audit, and nobody wants to spend more time on an audit than they have to. Your best bet is to choose an audit partner that has an audit management platform, like A-SCEND. Audit management platforms can simplify and accelerate your path to a quality audit, further reduce time spent on repetitive tasks, and integrate with GRC tools to work where you do.
Interested in how A-LIGN can help your organization consolidate your SOC 2 and ISO 27001 audits? Contact us today to learn more.
Cybersecurity threats evolve every day, and organizations must adopt proactive strategies to stay ahead. While red and blue teaming have been staples in cybersecurity, purple teaming is emerging as a collaborative approach to bridge the gap between offensive and defensive security. But what exactly is purple teaming, and how can it enhance your organization’s security posture?
What is purple teaming?
Purple teaming is collaborative cybersecurity exercise that integrates the efforts of red and blue teams to improve an organization’s overall security. Unlike traditional red or blue team exercises, purple teaming emphasizes communication and coordination, ensuring both teams work together to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Red Teams simulate attackers to identify weaknesses. They design and execute adversarial campaigns, like phishing or exploiting security gaps, to test both human and technical defenses. Red teaming is all about uncovering the human element—can they trick staff with phishing emails, and will their efforts go undetected?
- Blue Teams assess and strengthen defenses. Their focus is on monitoring systems, detecting threats, and responding to security incidents. Blue teams look closely at what activities can be detected and work to improve overall visibility and response.
- Purple Teams integrate the efforts of the Red and Blue teams to ensure a collaborative, holistic security approach. They work together and communicate openly, providing a comprehensive understanding of an organization’s strengths and weaknesses.
A Purple Team Exercise is a full-knowledge engagement — meaning attack activity is exposed and explained as it happens. Red and Blue teams work together with an open discussion about each attack technique and defense expectation to improve people, process, and technology in real-time.
When should you use purple teaming?
Purple teaming is particularly beneficial for organizations that:
- Want to enhance collaboration between offensive and defensive teams.
- Aim to improve detection and response capabilities in real-time.
- Seek a holistic approach to security that combines the strengths of red and blue teams.
- Operate in industries with high-security demands, such as finance, healthcare, or government.
What is the process of a Purple Team exercise?
A purple team exercise is a structured, iterative process designed to test and improve security controls. Here’s how it typically unfolds:
- Introduction of adversary and TTPs
An Exercise Coordinator introduces the adversary, outlining their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), and provides technical details for the exercise. - Table-top discussion
Teams discuss security controls and expectations for the TTPs being tested. - Attack simulation
The red team emulates the TTPs, simulating real-world adversary behavior. - Detection & response
The blue team follows established processes to detect and respond to the simulated attacks, sharing screens to review alerts, logs, and forensic artifacts. - Documentation & tuning
Results are documented, highlighting what worked and what didn’t. Security controls are adjusted or tuned to increase visibility. - Iterate & improve
The process is repeated for the next TTP, incorporating lessons learned and additional action items.
What are the benefits of purple teaming?
Purple teaming offers several advantages for organizations looking to strengthen their cybersecurity:
- Enhanced collaboration
By fostering communication between red and blue teams, purple teaming breaks down silos and promotes a unified approach to security. - Improved detection & response
Real-time collaboration helps identify gaps in detection and response processes, enabling teams to address them more effectively. - Holistic security evaluation
Purple teaming evaluates people, processes, and technology, providing a comprehensive view of an organization’s security posture. - Actionable insights
The iterative nature of purple teaming ensures continuous improvement, with actionable recommendations to enhance security controls.
Bridging the gap for better security
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, organizations must adopt innovative approaches to stay secure. Purple teaming represents the next step in proactive cybersecurity, combining the strengths of red and blue teams to create a collaborative, holistic defense strategy. By integrating offensive and defensive efforts, purple teaming not only identifies vulnerabilities but also strengthens an organization’s ability to detect, respond to, and prevent attacks.
Organizations cannot afford to leave their clients’ trust to chance. They face complex pressures from customers, regulators and cyberattacks to implement appropriate controls within their environments to protect customer and proprietary data. For many organizations, SOC reports play an integral role in demonstrating an organization’s level of commitment – exemplifying how it will gain their customers’ trust. A SOC report helps to show an organization has identified the key threats and vulnerabilities that pose a risk to its operations and customers, and has implemented an internal controls framework to address those risks. Keep reading to learn about the types of SOC reports and understand the difference between SOC 1 vs SOC 2.
What is a SOC report?
A System and Organization Controls (SOC) attestation is a signed report produced by an independent Certified Public Accountant (CPA). The SOC report includes the overall processes and controls as described by the organization and the auditor’s assessment of the controls, at a point in time or over a period of time.
Organizations rely on SOC reports to demonstrate to customers, vendors, and stakeholders that they have the appropriate policies, procedures, and controls in place to manage and mitigate the key threats and vulnerabilities that pose a risk to their environment. Companies are asked by their clients to provide them with a SOC report to prove:
- Its internal controls environment is implemented and operating effectively such that the financially relevant systems can be relied upon; or
- Its internal controls environment is implemented and operating effectively as it relates to the security, confidentiality, availability, processing accuracy or privacy of data.
Since organizations can potentially be held liable for inaccurate financial reporting, security breaches, disclosure of confidential or private information, system downtime, and incorrect processing of transactions, SOC reports have become a method for organizations across a wide range of industries to show that these risks has been considered and addressed.
SOC 1 vs SOC 2 vs SOC 3
There are three different SOC reports available, all of which have a different focus and use. They do not represent a progression (e.g., a SOC 2 report isn’t “better” than a SOC 1 report), but instead address different risks and needs for the organization.
SOC 1
A SOC 1 report follows the guidance outlined in the Statement on Standards for Attestation Agreements, which focuses on the internal controls that have an impact on the financially relevant systems and reporting. The main goal of a SOC 1 report is to ensure the controls identified by the organization are in place and/or operating effectively to appropriately address the risk of inaccurately reporting financials. The scope of a SOC 1 audit is more limited than its counterparts but plays a vital role in establishing trust between a service organization and its user entities that rely on its controls for financial statement accuracy.
In contrast to SOC 2, which addresses broader security initiatives, SOC 1 is specifically designed for organizations whose services directly impact the financial reporting of their customers, such as payroll processors, cloud service providers handling financial data, and HR technology platforms.
SOC 2
A SOC 2 report can be used by a number of organizations that provide some sort of service (e.g. SaaS, colocation, data hosting, etc.) to another. While it addresses risks associated with the handling and access of data, it isn’t a cybersecurity assessment that evaluates specific technical configurations (although a SOC for Cybersecurity report does). A SOC 2 report focuses more on how an organization implements and manages controls to mitigate the identified risks to the different parts of an organization.
The SOC 2 audit testing framework is based on the Trust Services Criteria (TSC), which are used to identify various risks (points of focus) an organization should consider addressing. Based on the TSCs the organization selects to be in-scope, the third-party compliance and audit firm evaluates whether the organization has the appropriate policies, procedures and controls in place to manage the identified risks effectively.
There are five Trust Services Criteria. The first criteria, Security, must be included with every SOC 2 report and is referred to as the “Common Criteria”.
- Security
- Availability
- Processing Integrity
- Confidentiality
- Privacy
When considering the SOC 1 vs SOC 2 difference, the important thing to remember is that a SOC 1 report is geared towards financial reporting controls, while a SOC 2 audit evaluates operational risk management in terms of data protection.
SOC 3
A SOC 3 report is coupled with a SOC 2 report and is a scaled-down version of the SOC 2 report. The report is intended for a broader public audience including prospective customers and stakeholders. The SOC 2 report provides greater detail regarding the organization’s controls and operations. A SOC 3 report is effectively a summary of the SOC 2 report that provides less technical information, making it suitable for an organization to share publicly on its website or to hand out to prospective customers.
Understanding SOC report types
SOC 1 and 2 reports vary by two distinct types referred to as “Type 1” or “Type 2.” A type 1 attestation is a point in time or “snapshot” of controls designed and implemented as of a specific date. A type 1 assesses whether or not those controls are appropriate for the risks facing the organization, but does not provide an evaluation of how effective they are over a period of time. That’s because it’s only looking at the controls as they exist at that given date.
On the other hand, a type 2 attestation assesses whether the controls were designed and operating effectively over a specified period. The compliance and audit firm typically issue type 2 reports for durations of three, six, nine, or twelve months. Type 2 reports covering a shorter duration provide less value to the readers of the report regarding the operational effectiveness of the controls in place. Understandably, a Type 2 report takes longer to complete and provides a more thorough evaluation of operational performance.
Elevate your compliance with A-LIGN
As a licensed CPA firm with more than 20 years of experience when it comes to SOC reports, A-LIGN has the people, process, and platform you need to help your organization reach the summit of your potential as it pertains to compliance. Our strategic approach to compliance can help you meet the risks over a broad range of frameworks, making it easy to meet multiple standards without starting from scratch ahead of every audit.
Joining the ranks of SOC 2 certified companies demonstrates your commitment to a high level of security. Plus, many companies require a SOC 2 certification just to do business with them.
Learning about the SOC 2 controls is the first step to understanding this popular framework. But where do you go from there? The best way to accomplish your goal of SOC 2 certification is with the right audit partner.
Keep reading to learn why these SOC 2 certified companies chose A-LIGN as their trusted audit partner.
SOC 2 certified companies


Environics Analytics Utilizes Cybersecurity Compliance Certifications to Provide a Trusted Data Ecosystem to Canadian Organizations
Environics Analytics (EA) is a leading data analytics and marketing services company, helping clients achieve results through evidence-based decisions. As the leading source for data in Canada, EA wanted to establish a process that would keep EA at the forefront of compliance.
“Data security and integrity is top of mind for Canadian businesses across every sector,” said James Smith, Chief Compliance Officer for EA. “Organizations rely on us to manage data securely. Audits are essential to providing the assurance that our team is maintaining the highest operational standards.”
The first call James made was to their data center supplier located in Toronto, Canada.
“I knew our data center supplier was SOC 2 compliant, so I wanted to better understand their approach – the examination, process, and recommended providers,” he said. “A-LIGN came up immediately in the conversation and they had nothing but great things to say about the auditing firm. They then sent over their issued SOC 2 report, which was well executed and highly detailed.”
After speaking with A-LIGN, James felt confident he found the right fit in an auditing firm and decided to move forward with their first endeavor, a SOC 2 gap assessment. Following the initial gap assessment in 2016, Environics Analytics went on to earn their CSAE 3416 certification, SOC 1 report, SOC 2 report, HIPAA certification and conducted penetration testing.
“A-LIGN has a very consultative approach to auditing and truly provides the human element,” said James. “As the saying goes, ‘don’t know what you don’t know’ and that was very true for us throughout the various audits. The auditors are happy to provide guidance along the way and I have always found them to be fair.”
EA has found value in consistency over the years with the ability to pick up where they left off with the A-LIGN team, resulting in a seamless auditing experience.
To learn how A-LIGN can help your organization earn a high-quality SOC 2 report, contact us today.


Menlo Security reduces evidence collection time by 60% with consolidated audit approach
Menlo Security chose A-LIGN as their audit partner to accomplish ISO/IEC 27001, ISO 27017, ISO 27018, and SOC 2 compliance.
By combining their ISO 27001 and SOC 2 engagements together, the Menlo team achieved impressive efficiency—cutting evidence collection time by 60% while delivering fast, impactful results.
“I am very proud that Menlo Security and A-LIGN worked together to consolidate our SOC 2 and ISO 27001 assessments at the same time to reduce time, resources, and costs. This process has been carefully planned, communicated, and executed with a high degree of success.”
-Rashpal Singh, Global Director of Governance, Risk, and Compliance, Menlo Security


Why SOC 2 certified companies choose A-LIGN
A-LIGN is the top issuer of SOC 2 audits in the world. There’s a reason why. Our highly experienced auditors can provide your organization with guidance, tools, and a premium quality audit for your SOC 2 attestation. By the numbers, the A-LIGN difference is:
- #1 SOC 2 issuer in the world
- 17.5k+ SOC assessments completed
- 96% client satisfaction rating
- 200+ SOC auditors globally
Are you ready to get started on your organization’s path to SOC 2 certification? Contact us today to get started on your compliance journey and learn why these companies choose A-LIGN as their trusted audit partner.